💪 git-machete is a robust tool that simplifies your git workflows.
🦅 The bird's eye view provided by git-machete makes merges/rebases/push/pulls hassle-free
even when multiple branches are present in the repository
(master/develop, your topic branches, teammate's branches checked out for review, etc.).
🎯 Using this tool, you can maintain small, focused, easy-to-review pull requests with little effort.
👁 A look at a git machete status gives an instant answer to the questions:
- What branches are in this repository?
- What is going to be merged (rebased/pushed/pulled) and to what?
🚜 git machete traverse semi-automatically traverses the branches, helping you effortlessly rebase, merge, push and pull.
🔌 See also VirtusLab/git-machete-intellij-plugin — a port into a plugin for the IntelliJ Platform products, including PyCharm, WebStorm etc.
We provide a couple of alternative ways of installation. See PACKAGES.md for the full list.
git-machete requires Python >= 3.6. Python 2.x is no longer supported.
brew install git-macheteYou need to have Python and pip installed from system packages.
For user-wide install:
pip install --user git-machetePlease verify that your PATH variable has ${HOME}/.local/bin/ included.
For system-wide install:
sudo -H pip install git-machete # system-wide installTip: pass an extra -U flag to pip install to upgrade an already installed version.
conda install -c conda-forge git-machetescoop install git-macheteTip: check the guide on installing snapd if you don't have Snap support set up yet in your system.
sudo snap install --classic git-macheteIt can also be installed via Ubuntu Software (simply search for git-machete).
Note: classic confinement is necessary to ensure access to the editor installed in the system (to edit e.g. .git/machete file or rebase TODO list).
Tip: run sudo apt-get install -y software-properties-common first if add-apt-repository is not available on your system.
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:virtuslab/git-machete
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y python3-git-macheteCheck Repology for the available distro-specific packages.
On macOS and most Linux distributions, you can install via Nix:
nix-channel --add https://nixos.org/channels/nixos-unstable unstable # if you haven't set up any channels yet
nix-env -i git-macheteNote: since nixos-21.05, git-machete is included in the stable channels as well.
The latest released version, however, is generally available in the unstable channel.
Stable channels may lag behind; see repology for the current channel-package mapping.
The Pex tool (short for Python EXecutable) allows you to build "pex" files which are executable Python environments in a single file.
Assuming you have already installed the pex utility, you can build git-machete as a pex:
pex git-machete -m git_machete.bin:main -o git-machete
Then put the produced git-machete file somewhere on your PATH.
cd your-repo/
git machete discoverSee and possibly edit the suggested layout of branches.
Branch layout is always kept as a .git/machete text file, which can be edited directly or via git machete edit.
git machete status --list-commitsGreen edge means the given branch is in sync with its parent.
Red edge means it is out of sync — parent has some commits that the given branch does not have.
Gray edge means that the branch is merged to its parent.
git machete traverse --fetch --start-from=first-rootPut each branch one by one in sync with its parent and remote tracking branch.
git machete advanceUseful for merging the child branch to the current branch in a linear fashion (without creating a merge commit).
Check out the given PRs into local branches, also traverse chain of pull requests upwards, adding branches one by one to git-machete and check them out locally as well:
git machete github checkout-prs [--all | --by=<github-login> | --mine | <PR-number-1> ... <PR-number-N>]
git machete gitlab checkout-mrs [--all | --by=<gitlab-login> | --mine | <MR-number-1> ... <MR-number-N>]Create the PR/MR, using the upstream (parent) branch from .git/machete as the base:
git machete github create-pr [--draft]
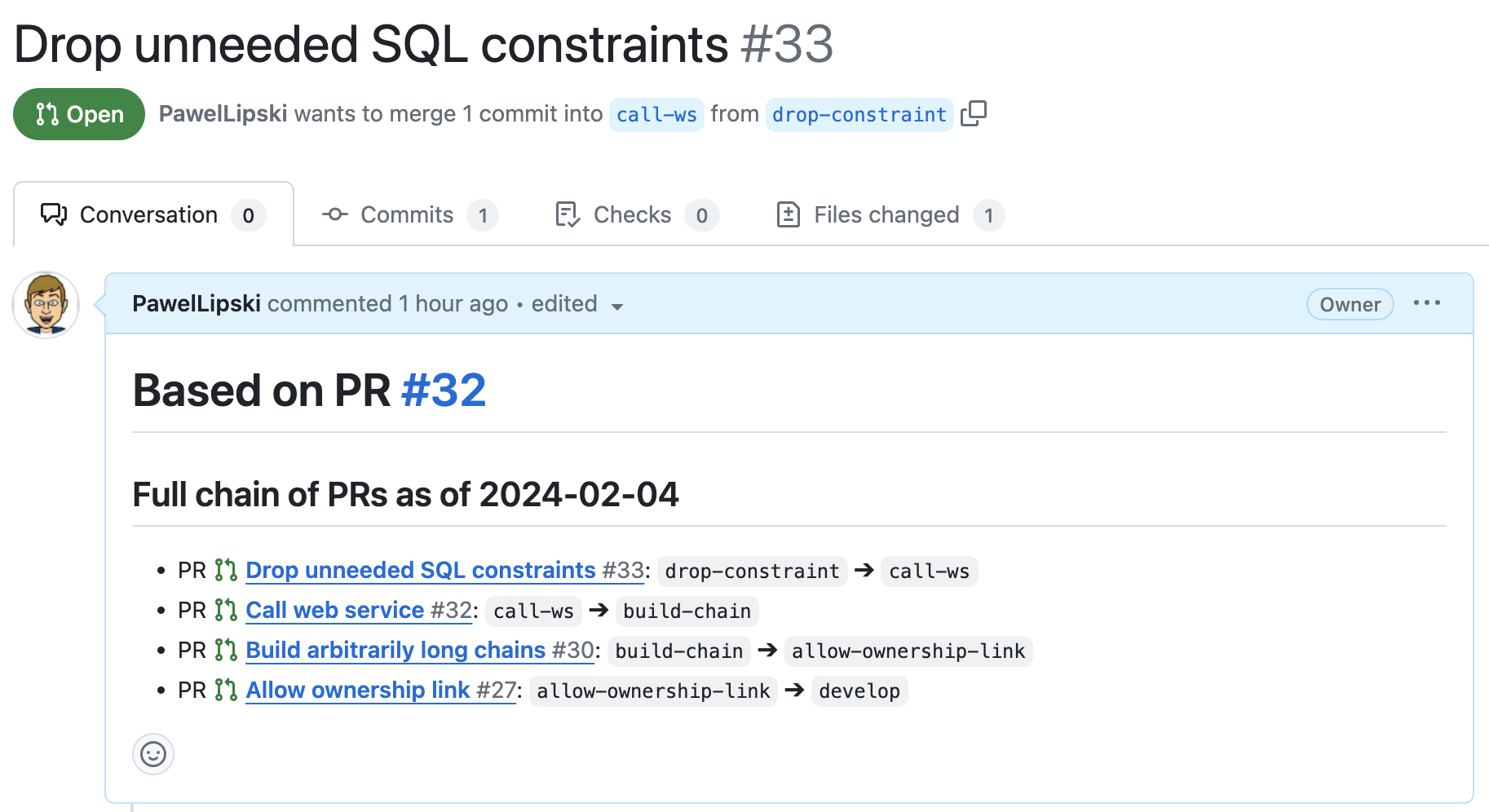
git machete gitlab create-mr [--draft]The entire chain of PRs/MRs will be posted in the PR/MR description (example for GitHub):
Note: for private repositories (or side-effecting operations like create-pr/create-mr on public repositories),
a GitHub API token with repo access or a GitLab API token with api access is required.
See the docs for github
or gitlab for how to provide the token.
When git-machete is installed via Homebrew (and a few other supported package managers, see PACKAGES.md),
shell completions should be installed automatically.
For other package managers (like pip), or when your shell doesn't pick up the Homebrew-installed completion, use the following:
Put the following into ~/.bashrc or ~/.bash_profile:
eval "$(git machete completion bash)" # or, if it doesn't work:
source <(git machete completion bash)Put the following into ~/.config/fish/config.fish:
git machete completion fish | sourcePut the following into ~/.zshrc:
eval "$(git machete completion zsh)" # or, if it doesn't work:
source <(git machete completion zsh)I've run git machete discover... but the branch layout I see in .git/machete doesn't exactly match what I expected. Am I doing something wrong?
No! It's all right, discover is based on an (imperfect)
heuristic
which usually yields branch layout close to what the user would expect.
It still might not be perfect and — for example — declare branches to be children of main/develop instead of each other.
Just run git machete edit to fix the layout manually.
If you're working on JetBrains IDEs, you can use git-machete IntelliJ plugin
to have branch name completion when editing .git/machete file.
Also, consider git machete github checkout-prs or git machete gitlab checkout-mrs
instead of git machete discover if you already have GitHub PRs/GitLab MRs opened.
There are two commonly used ways to put a branch back in sync with its base (parent) branch:
- rebase the branch onto its base branch
- merge the base branch into the branch
While git-machete supports merging base branch (like main) to update the branch
(git machete traverse --merge),
this approach works poorly with stacked PRs.
You might end up with a very tangled history very quickly, and a non-trivial sequence of git cherry-picks might be needed to restore order.
That is why we recommend using rebase over merge for stacked PRs. However, we still recommend using merge for the narrow case of backporting hotfixes.
Sometimes when I run update or traverse, too many commits are taken into the rebase... how to fix that?
Contrary to the popular misconception, git doesn't have a notion of "commits belonging to a branch". A branch is just a movable reference to a commit.
This makes it hard in general case to determine the range of commits that form the "unique history" of the given branch. There's an entire algorithm in git-machete for determining the fork point of the branch (i.e. the place after which the unique history of the branch starts).
One thing that you can do to help fork-point algorithm in its job, is to not delete local branches instantly after they're merged or discarded. They (or specifically, their reflogs) will be still useful for a while to determine fork points for other branches (and thus, the range of commits taken into rebase).
Also, you can always override fork point for a branch explicitly
with git machete fork-point --override-to... command.
Find the docs at Read the Docs.
You can also check git machete help and git machete help <command>.
For the excellent overview for the reasons to use small & stacked PRs, see Ben Congdon's blog post.
Take a look at git-machete reference blog post for a guide on how to use the tool.
The more advanced features like automated traversal, upstream inference and tree discovery are described in the second part of the series.
git-machete (since version 2.13.0) is compatible with git >= 1.8.0.
Contributions are welcome! See contributing guidelines for details.