import random
def partition(nums, left, right):
if left >= right:
return
pivot_idx = random.randint(left, right)
pivot = nums[pivot_idx]
nums[right], nums[pivot_idx] = nums[pivot_idx], nums[right]
partition_idx = left
for i in range(left, right):
if nums[i] < pivot:
nums[partition_idx], nums[i] = nums[i], nums[partition_idx]
partition_idx += 1
nums[right], nums[partition_idx] = nums[partition_idx], nums[right]
partition(nums, partition_idx + 1, right)
partition(nums, left, partition_idx - 1)
return
def quicksort(A):
partition(A, 0, len(A) - 1)
return A
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = [7, 6, 8, 5, 2, 1, 3, 4, 0, 9, 10]
print(a)
print(quicksort(a))def merge(A, B):
C = []
i, j = 0, 0
while i < len(A) and j < len(B):
if A[i] <= B[j]:
C.append(A[i])
i += 1
else:
C.append(B[j])
j += 1
if i < len(A):
C += A[i:]
if j < len(B):
C += B[j:]
return C
def mergsort(A):
n = len(A)
if n < 2:
return A[:]
left = mergsort(A[:n // 2])
right = mergsort(A[n // 2:])
return merge(left, right)
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = [7, 6, 8, 5, 2, 1, 3, 4, 0, 9, 10]
print(a)
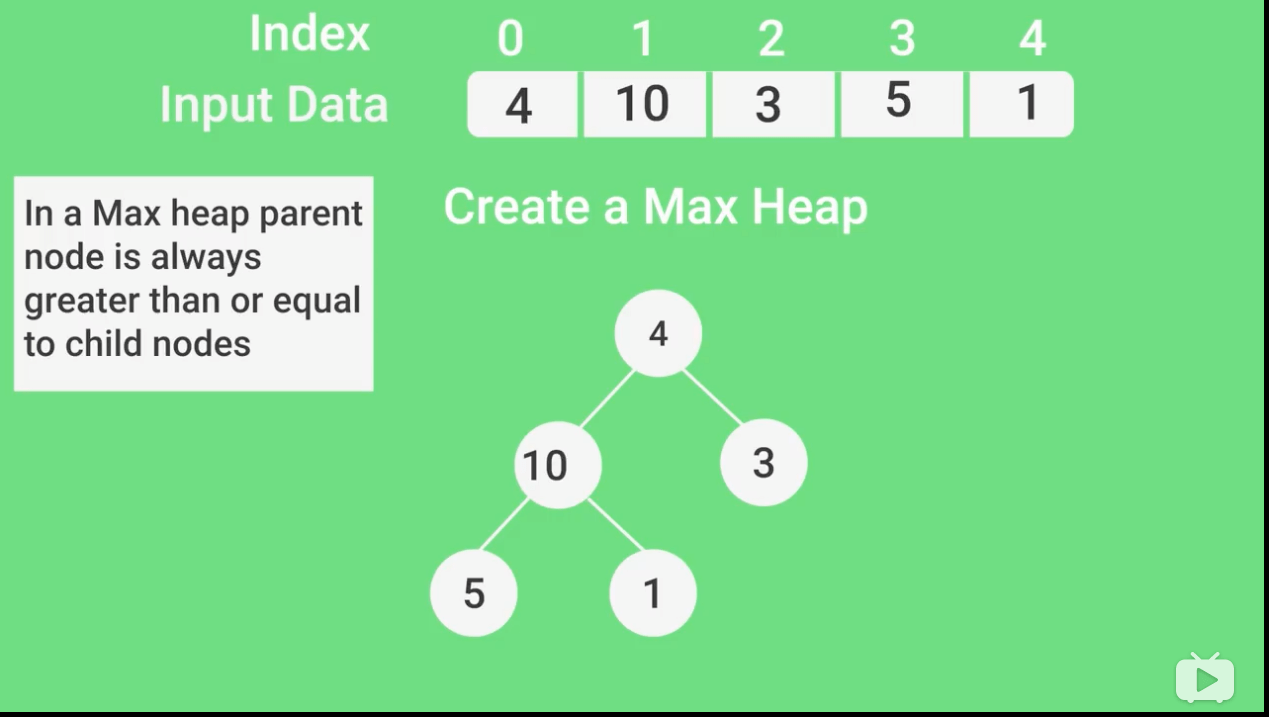
print(mergsort(a))用数组表示的完美二叉树 complete binary tree
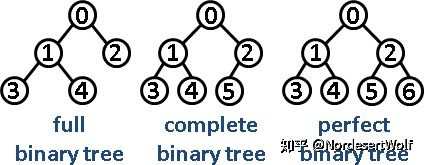
完美二叉树 VS 其他二叉树
核心代码
def heap_adjust(A, start=0, end=None):
if end is None:
end = len(A)
while start is not None and start < end // 2:
l, r = start * 2 + 1, start * 2 + 2
swap = None
if A[l] > A[start]:
swap = l
if r < end and A[r] > A[start] and (swap is None or A[r] > A[l]):
swap = r
if swap is not None:
A[start], A[swap] = A[swap], A[start]
start = swap
return
def heapsort(A):
# construct max heap
n = len(A)
for i in range(n // 2 - 1, -1, -1):
heap_adjust(A, i)
# sort
for i in range(n - 1, 0, -1):
A[0], A[i] = A[i], A[0]
heap_adjust(A, end=i)
return A
# test
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = [7, 6, 8, 5, 2, 1, 3, 4, 0, 9, 10]
print(a)
print(heapsort(a))-
思路 1: sort 后取第 k 个,最简单直接,复杂度 O(N log N) 代码略
-
思路 2: 使用最小堆,复杂度 O(N log k)
class Solution:
def findKthLargest(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> int:
# note that in practice there is a more efficient python build-in function heapq.nlargest(k, nums)
min_heap = []
for num in nums:
if len(min_heap) < k:
heapq.heappush(min_heap, num)
else:
if num > min_heap[0]:
heapq.heappushpop(min_heap, num)
return min_heap[0]- 思路 3: Quick select,方式类似于快排,每次 partition 后检查 pivot 是否为第 k 个元素,如果是则直接返回,如果比 k 大,则继续 partition 小于 pivot 的元素,如果比 k 小则继续 partition 大于 pivot 的元素。相较于快排,quick select 每次只需 partition 一侧,因此平均复杂度为 O(N)。
class Solution:
def findKthLargest(self, nums: List[int], k: int) -> int:
k -= 1 # 0-based index
def partition(left, right):
pivot_idx = random.randint(left, right)
pivot = nums[pivot_idx]
nums[right], nums[pivot_idx] = nums[pivot_idx], nums[right]
partition_idx = left
for i in range(left, right):
if nums[i] > pivot:
nums[partition_idx], nums[i] = nums[i], nums[partition_idx]
partition_idx += 1
nums[right], nums[partition_idx] = nums[partition_idx], nums[right]
return partition_idx
left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1
while True:
partition_idx = partition(left, right)
if partition_idx == k:
return nums[k]
elif partition_idx < k:
left = partition_idx + 1
else:
right = partition_idx - 1- 手写快排、归并、堆排序