You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
consttree=newElement('div',{classname: 'div'},[newElement('h1',{style: 'color: red;'},['Hello, This is my Vdom library']),newElement('ul',[newElement('li',['1111']),newElement('li',['2222']),])]);const$dom=tree.render();console.log(111,$dom);
对于一颗二叉树,深度优先搜索(Depth First Search)是沿着树的深度遍历树的节点,尽可能深的搜索树的分支。以上面二叉树为例,深度优先搜索的顺序为:ABDECFG。怎么实现这个顺序呢 ?深度优先搜索二叉树是先访问根结点,然后遍历左子树接着是遍历右子树,因此我们可以利用堆栈的先进后出的特点,现将右子树压栈,再将左子树压栈,这样左子树就位于栈顶,可以保证结点的左子树先与右子树被遍历。
广度优先搜索(Breadth First Search),又叫宽度优先搜索或横向优先搜索,是从根结点开始沿着树的宽度搜索遍历,上面二叉树的遍历顺序为:ABCDEFG.
// 1.构建虚拟DOMconsttree=newElement('div',{classname: 'div'},[newElement('h1',{style: 'color: red;'},['Hello, This is my Vdom library']),newElement('ul',[newElement('li',['1111']),newElement('li',['2222']),])]);// 2.通过虚拟DOM构建真正的DOMconst$dom=tree.render();const$app=document.querySelector('#app');$app.replaceWith($dom);// 3.生成新的虚拟DOMconstnewTree=newElement('div',{id: 'div1'},[newElement('h1',{style: 'color: red;'},['Hello, This is my vdom library111']),newElement('p',{style: 'color: blue;'},['extra text']),newElement('ul',[newElement('li',['1111']),newElement('li',['5555']),newElement('li',['333']),])]);// 4.比较新旧虚拟DOM树的差异constpatches=diff(tree,newTree);// 5.根据变化了的部分去更新DOMpatch($dom,patches);
前言
之前写过一篇文章为什么使用v-for时必须添加唯一的key?,但是解释的不是很深刻,其实真正的原因还需要从Virtual DOM的实现上解释;本篇文章从简单实现一个Virtual DOM入手,去解释一下Virtual DOM的实现思想;
源码地址:github
思路
1.定义一个类,用来创建 DOM 元素(element.js);
2.比较新旧 DOM 树的差异(diff.js);
3.将差异的部分渲染到DOM树即只渲染变化了的部分(patch.js)
virtural-dom的模型
一个DOM标签所需的基本元素
过程
一. 用javascript对象表示DOM结构
为了实现这个需求,下面使用element.js。
原理:
1.根据 tagName 使用
document.createElement创建元素2.根据 props 使用
setAttribute给元素设置属性3.根据 innerHtml 使用
document.createTextNode渲染文本节点4.根据是否有 children (子元素) 去递归渲染
5.最后使用
appendChild将创建的元素插入到页面中然后代码和使用方式如下
element.js
这跟vue的render方法很相似
vue中也是把template解析成render模板进行渲染的;
二. 比较新旧 DOM树的差异
差异类型
对DOM的操作也就是对节点的增删改查操作,当前定义了如下几种类型
深度优先遍历,记录差异
对于一颗二叉树,深度优先搜索(Depth First Search)是沿着树的深度遍历树的节点,尽可能深的搜索树的分支。以上面二叉树为例,深度优先搜索的顺序为:ABDECFG。怎么实现这个顺序呢 ?深度优先搜索二叉树是先访问根结点,然后遍历左子树接着是遍历右子树,因此我们可以利用堆栈的先进后出的特点,现将右子树压栈,再将左子树压栈,这样左子树就位于栈顶,可以保证结点的左子树先与右子树被遍历。
广度优先搜索(Breadth First Search),又叫宽度优先搜索或横向优先搜索,是从根结点开始沿着树的宽度搜索遍历,上面二叉树的遍历顺序为:ABCDEFG.
1.比较属性的变化
遍历旧的属性,找到被删除和修改的情况
遍历新元素的属性,找到添加的属性
2.比较子元素的变化
3.比较innerHTML的变化
使用pathes 来存储差异
完整代码如下
diff.js
需要注意的是,因为tagName是重复的,不能用这个进行对比,所以需要给子节点加上唯一的标识key,列表对比的时候,使用key进行对比,这样才能复用老的DOM树上的节点;
求最小的插入,删除操作的组合;这个问题抽象出来其实是字符串的最小编辑距离问题(Edition Distance),最常见的解决算法是 Levenshtein Distance,通过动态规划求解。我们需要优化一下最常见的操作;具体的实现算法也很多;
vue和react的虚拟DOM的Diff算法大致相同,其核心是基于两个简单的假设:
引用React’s diff algorithm中的例子:
当某一层有很多相同的节点时,也就是列表节点时,Diff算法的更新过程默认情况下也是遵循以上原则。
比如一下这个情况:
我们希望可以在B和C之间加一个F,Diff算法默认执行起来是这样的:
即把C更新成F,D更新成C,E更新成D,最后再插入E,是不是很没有效率?
所以我们需要使用key来给每个节点做一个唯一标识,Diff算法就可以正确的识别此节点,找到正确的位置区插入新的节点。
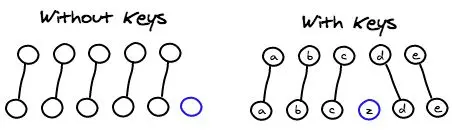
所以一句话,key的作用主要是为了高效的更新虚拟DOM。另外vue中在使用相同标签名元素的过渡切换时,也会使用到key属性,其目的也是为了让vue可以区分它们,否则vue只会替换其内部属性而不会触发过渡效果。
三.将差异的部分渲染到DOM树即只渲染变化了的部分
通过深度优先遍历,记录差异 patches,最后需要根据patches进行DOM操作;
paches记录了差异的类型;大致数据结构如下:
实现该过程的完整代码如下:
patch.js
最后测试一下
总结
1.关键的几个文件就是: element.js, diff.js, patch.js;
2.github上有很多Virtual DOM实现的例子,博主也是参考了一下其他人的实现,感兴趣的可以去搜索看一下,或者自己实现一个
参考
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered: