Aced is a tool to parse and resolve a single targeted Active Directory principal's DACL. Aced will identify interesting inbound access allowed privileges against the targeted account, resolve the SIDS of the inbound permissions, and present that data to the operator. Additionally, the logging features of pyldapsearch have been integrated with Aced to log the targeted principal's LDAP attributes locally which can then be parsed by pyldapsearch's companion tool BOFHound to ingest the collected data into BloodHound.
I wrote Aced simply because I wanted a more targeted approach to query ACLs. Bloodhound is fantastic, however, it is extremely noisy. Bloodhound collects all the things while Aced collects a single thing providing the operator more control over how and what data is collected. The case for detection is reduced by only querying for what LDAP wants to tell you and by not performing an action known as "expensive ldap queries". Aced has the option to forego SMB connections for hostname resolution. You have the option to prefer LDAPS over LDAP. With the additional integration with BloodHound, the collected data can be stored in a familiar format that can be shared with a team. Privilege escalation attack paths can be built by walking backwards from the targeted goal.
Thanks to the below for all the code I stole:
@_dirkjan
@fortaliceLLC
@eloygpz
@coffeegist
@tw1sm
└─# python3 aced.py -h
_____
|A . | _____
| /.\ ||A ^ | _____
|(_._)|| / \ ||A _ | _____
| | || \ / || ( ) ||A_ _ |
|____V|| . ||(_'_)||( v )|
|____V|| | || \ / |
|____V|| . |
|____V|
v1.0
Parse and log a target principal's DACL.
@garrfoster
usage: aced.py [-h] [-ldaps] [-dc-ip DC_IP] [-k] [-no-pass] [-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH] [-aes hex key] [-debug] [-no-smb] target
Tool to enumerate a single target's DACL in Active Directory
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
Authentication:
target [[domain/username[:password]@]<address>
-ldaps Use LDAPS isntead of LDAP
Optional Flags:
-dc-ip DC_IP IP address or FQDN of domain controller
-k, --kerberos Use Kerberos authentication. Grabs credentials from ccache file (KRB5CCNAME) based on target parameters. If valid
credentials cannot be found, it will use the ones specified in the command line
-no-pass don't ask for password (useful for -k)
-hashes LMHASH:NTHASH
LM and NT hashes, format is LMHASH:NTHASH
-aes hex key AES key to use for Kerberos Authentication (128 or 256 bits)
-debug Enable verbose logging.
-no-smb Do not resolve DC hostname through SMB. Requires a FQDN with -dc-ip.
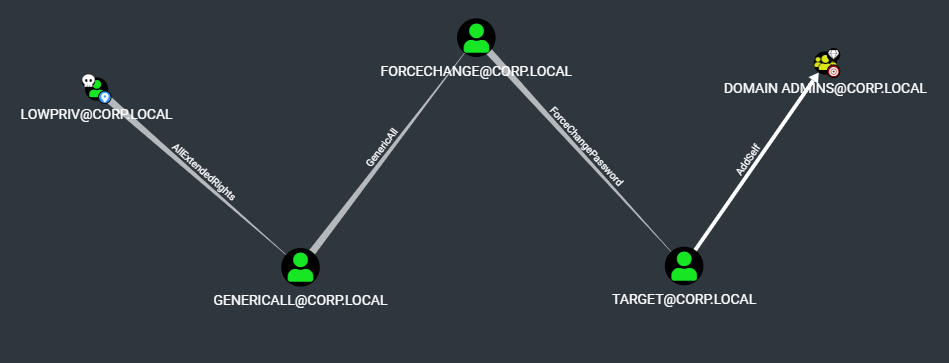
In the below demo, we have the credentials for the corp.local\lowpriv account. By starting enumeration at Domain Admins, a potential path for privilege escalation is identified by walking backwards from the high value target.

And here's how that data looks when transformed by bofhound and ingested into BloodHound.