./build
Optional: -d TASK_DEFN builds a docker image and pushes it to docker hub
(Example: java -jar poolgp-0.1.0-SNAPSHOT-standalone.jar -d full_games.json)
-d --demo PATHRuns in demo mode given configuration-e --eval PATHRuns in server mode with specified task definition-b --builder PATHOpens editing mode and writes to file provided (must exist)-t --tournament PATHRuns a tournament simulation if the given config contains a tournament key value pair (tournament config has a separate json format)-n --new FILENAMECreates a blank configuration file (with required fields) (this is meant to be subsequently edited)
Note: When running tournament mode, specify a normal run configuration (i.e. full_games.json) that contains a "tournament" entry specifying a tournament file (i.e. "tournament" : "tournament.json")
(Run lein deps)
[org.clojure/tools.cli "0.4.1"]
[org.clojure/core.async "0.4.490"]
[org.clojure/data.json "0.2.6"]
[clojush.poolgp "3.17.1-1-SNAPSHOT"] ;Note: this is the poolgp fork of clojush and contains new functions{
"simulation": {
"analysis" : [
{
"game" : {
"table" : {
"balls" : [
{"x" : 100, "y" : 150, "id" : 1, "type" : "striped"},
{"x" : 500, "y" : 285, "id" : "cue", "type" : "cue"}
]
}
}
},
],
"max-iterations" : 100000, (optional)
"watching" : 0, (optional)
"p1" : {
"strategy" : "(integer_**)"
},
"p2" : {
"strategy" : "(integer_+)"
}
},
"tournament" : "tournament.json", (optional)
"eval-worker" : {
"indiv-ingress" : 9999,
"indiv-egress" : 8000,
"opp-pool-req" : 8888,
"engine-hostname" : "engine"
}
}Tournament task defn structure:
{
"entrants" : [
{"id": "edfc5bb5-7d5b-4478-87e2-46165630aa0e", "strategy" : "(float_pop integer_mult float_mult boolean_not...)"},
{"id": "Ronnie O' Sullivan", "strategy" : "(float_pop float_mult integer_mult boolean_not...)"},
...
]
}Here is the structure for an individual being sent from Clojush to evaluation instances:
{:indiv indiv ;clojush.individual containing :program
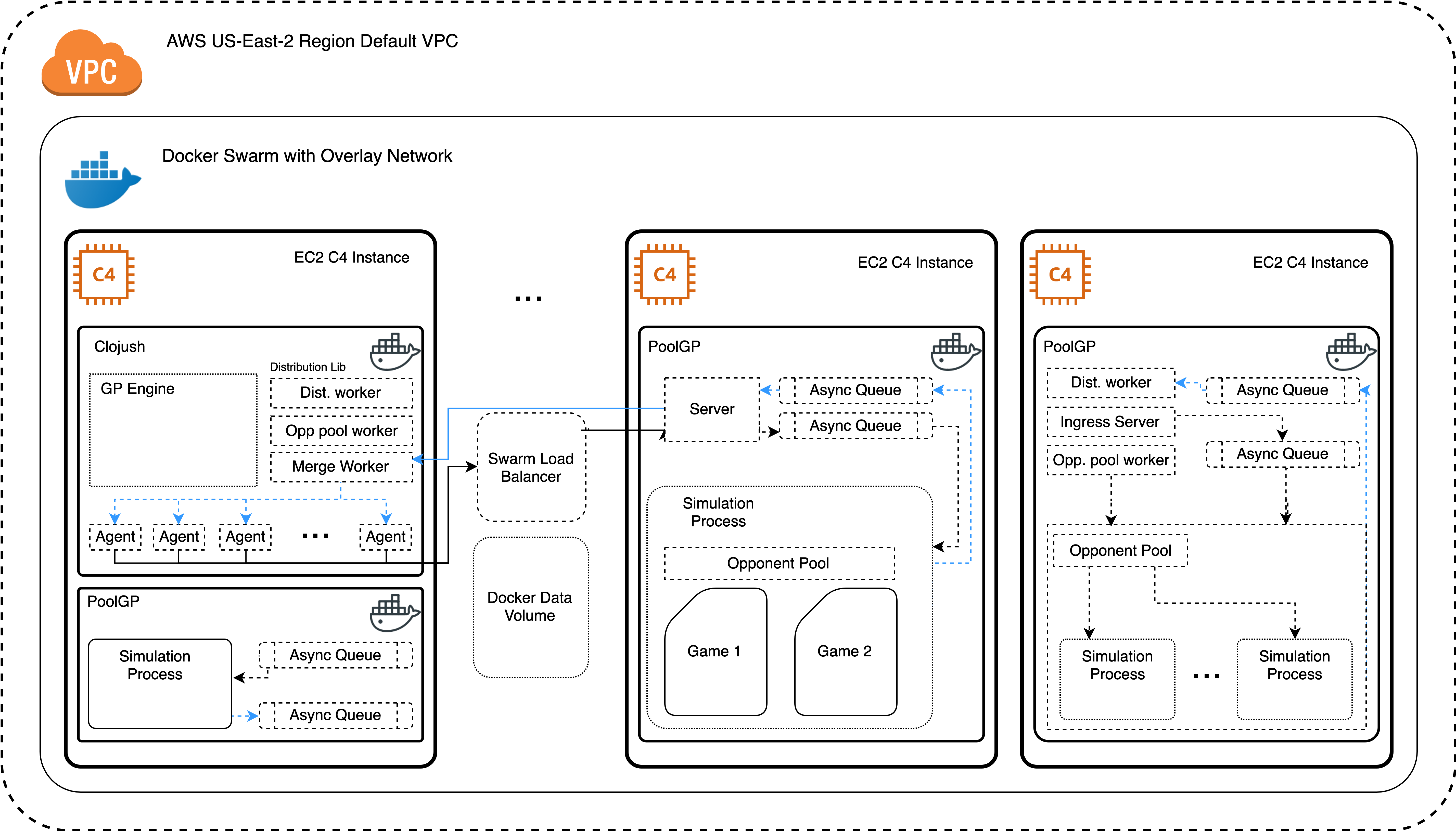
:cycle (int)}- Follow the tutorial on creating a Docker swarm.
- Copy
docker/docker-compose.ymlto the master node of your swarm - From the master node, run the following:
docker stack deploy --compose-file docker-compose.yml poolgpHere are the steps required for setting up Clojush for communication with PoolGP evaluation workers.
Add this dependency to your project.clj file: 
When your engine is ready to evaluate the entire population, include the following code:
In your ns declaration: (:require [poolgp.distribute :as poolgp])
(Note: this should be in clojush.src.pushgp.pushgp/compute-errors)
;temporary: wait 10 seconds for workers to start
(Thread/sleep 10000)
(poolgp/start-dist-services {
:incoming-port 8000
:outgoing-port 9999
:opp-pool-req-p 8888
:host "eval"})
;take first 10 individuals from starting gen if no
;previous gen computed
(let [prev-gen @POOLGP-PREV-GEN]
(poolgp/register-opponents
(take 10
(if (not (empty? prev-gen))
(sort-by :total-error prev-gen)
(map deref pop-agents)))))
(dorun (map #((if use-single-thread swap! send)
%1 poolgp/eval-indiv)
pop-agents))
(when-not use-single-thread (apply await pop-agents)) ;; SYNCHRONIZE
(let [opps (map deref pop-agents)]
(dorun (map #((if use-single-thread swap! send)
%1 evaluate-individual (fn [i] (poolgp/merge-fitness i opps)) %2
(assoc argmap :reuse-errors false))
pop-agents
rand-gens)))
(when-not use-single-thread (apply await pop-agents)) ;; SYNCHRONIZE
;(store generation)
(reset! POOLGP-PREV-GEN (doall (map deref pop-agents)))- Make sure you have an AWS account that can support charges incurred by running ec2 instances at high load. (These costs add up)
- Note: 8 c4.2xlarge instances requires a service limit increase from Amazon (support request)
- Create an ec2 keypair. In
ec2_launcher, rename the keypair argument with this keypair name. - Download the keypair pem file for use during deployment.
- Change the profile name in in
ec2_launcherto your own (remove arg if using default profile) - Determine the CIDR range of your default AWS VPC (or custom VPC)
- Determine the CIDR range to allow SSH access from (your IP)
- Execute:
ec2_launcher <keypair.pem> <ssh_cidr_block> <vpc_cidr_block> - Accept any SSH/SCP prompts
- This script will end by connecting you to the master node
- SSH into all nodes (including master) using public IP addresses or public DNS
- Run
./docker_installerand accept any prompts - From the master, execute
sudo docker swarm init --advertise-addr <instance_private_ip> --data-path-addr <instance_private_ip> - Then in all nodes, copy the outputted join command (run with sudo), and append
--advertise-addr <instance_private_ip> --data-path-addr <instance_private_ip> - make a directory called
logs - From master, execute
sudo docker stack deploy --compose-file docker-compose.yml poolgp - From there, list and inspect docker volumes to verify the location of log files
Copyright © 2018 Jack Hay
Distributed under the Eclipse Public License version 1.0