Because a null pointer does not point to a meaningful object, an attempt to access the data stored at that (invalid) memory location may cause a run-time error or immediate program crash. This is the null pointer error. It is one of the most common types of software weaknesses,[1] and Tony Hoare, who introduced the concept, has referred to it as a "billion dollar mistake" .
In 2009, Tony Hoare stated[15] that he invented the null reference in 1965 as part of the ALGOL W language. In that 2009 reference Hoare describes his invention as a "billion-dollar mistake":
I call it my billion-dollar mistake. It was the invention of the null reference in 1965. At that time, I was designing the first comprehensive type system for references in an object oriented language (ALGOL W). My goal was to ensure that all use of references should be absolutely safe, with checking performed automatically by the compiler. But I couldn't resist the temptation to put in a null reference, simply because it was so easy to implement. This has led to innumerable errors, vulnerabilities, and system crashes, which have probably caused a billion dollars of pain and damage in the last forty years.
Null values have a notorious reputation in the programming world, often leading to runtime errors and unexpected behavior. In response, functional programming languages like Haskell, OCaml, and F# have adopted a different approach to value representation, favoring the Option types, represented as None | Some a in these languages, over traditional null values.
The Option types, while often perceived as complex for beginners, can be conceptualized using the analogy of lists or arrays . Consider a container structure that can either be empty, represented by [] , or contain a value, represented by [a] .The Option types introduce an extended concept:
| Lists/Arrays | Option Types |
|---|---|
[] |
None |
[a] |
Some a |
Appearently, the Option types can be useful, but they can also lead to unnecessarily complex structures.
Consider a Cell .
This can be represented by
-
[0] -
Some 0
In a case the cell is empty,
This can be represented by
-
[] -
None
This system works so far.
However, the List or Option type can be easily nested such as:
-
[[0]] -
Some (Some 0)
corresponds to:
or
-
[[]] -
Some None
corresponds to:
What we need is not a nested Cell that is weired and meaningless but simply an empty Cell .
TypeScript cleverly avoids the complexity of nested Option types by employing the Nullable types instead.
Let's explore an example of a VSCode Extension that requires extracting the text from the active text editor.
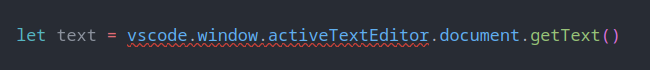
vscode.window.activeTextEditor.document.getText() is the adequate API, in TypeScript.
The TypeScript compiler is issuing errors and warnings.
The problem is:
'vscode.window.activeTextEditor' is possibly 'undefined'.
In JavaScript, undefined signifies a variable that has been declared but not yet assigned a value. While both undefined and null exist in the language with slight differences, we won't delve into those details here. For our purposes, we can consider undefined to be similar to null in a general sense.
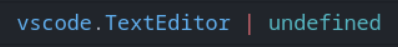
To visualize, it's like this!
Since VS Code users can close all tabs in the editor, vscode.window.activeTextEditor might become undefined .
The situation with vscode.window.activeTextEditor becoming undefined is similar to having an empty cell in a spreadsheet . Both represent the absence of a value we might expect to be present.
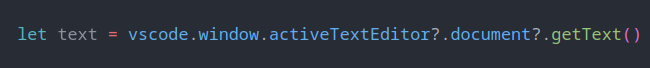
So, the proper type should be as below:
This is the Nullable type and what we really need.
In Functional Programming, everything is an expression or operation (💡 What is Functional Programming?).
When constructing expressions for mathematically consistent algebraic structures, it is essential to employ the correct types and their corresponding operators .
The concept of null references being a "billion-dollar mistake" stems from the lack of a well-designed null type and corresponding operators for programmers to use effectively.
In this case, we should use Optional chaining ( ?. ) operator in JavaScript(ES2020)/TypeScript
The optional chaining (
?.) operator accesses an object's property or calls a function. If the object accessed or function called using this operator isundefinedornull, the expression short circuits and evaluates toundefinedinstead of throwing an error.
Accordingly, the TypeScript code with the error should be fixed as below:
While the naming convention "optional chaining" evokes Option types, its actual behavior differs from nested Option types. Unlike Option types, which allow values to be either Some(value) or None, nullable chaining deals with values that can either be valid values or null. Therefore, "nullable chaining" might be a more accurate and descriptive name.