Important
Use this as a starting point for your own deployment. It is not recommended to use this in production as it only provides as simple deployment strategies.
Docker Stack deployment for MinIO Object Storage.
It supports both single and distributed deployments. It uses Docker volumes to store the data. And ensure the server is spread evenly across the nodes.
As a recommendation, you should only have MinIO deployed per Docker Swarm Cluster.
Before you can deploy MinIO, you need to carefully plan your deployment.
- Consider how many MinIO instances you want to deploy.
- Node placement for each MinIO instance.
- Storage driver for the volumes.
- How much storage you want to allocate to each instance.
- etc...
Here are some useful tips to help you plan your deployment.
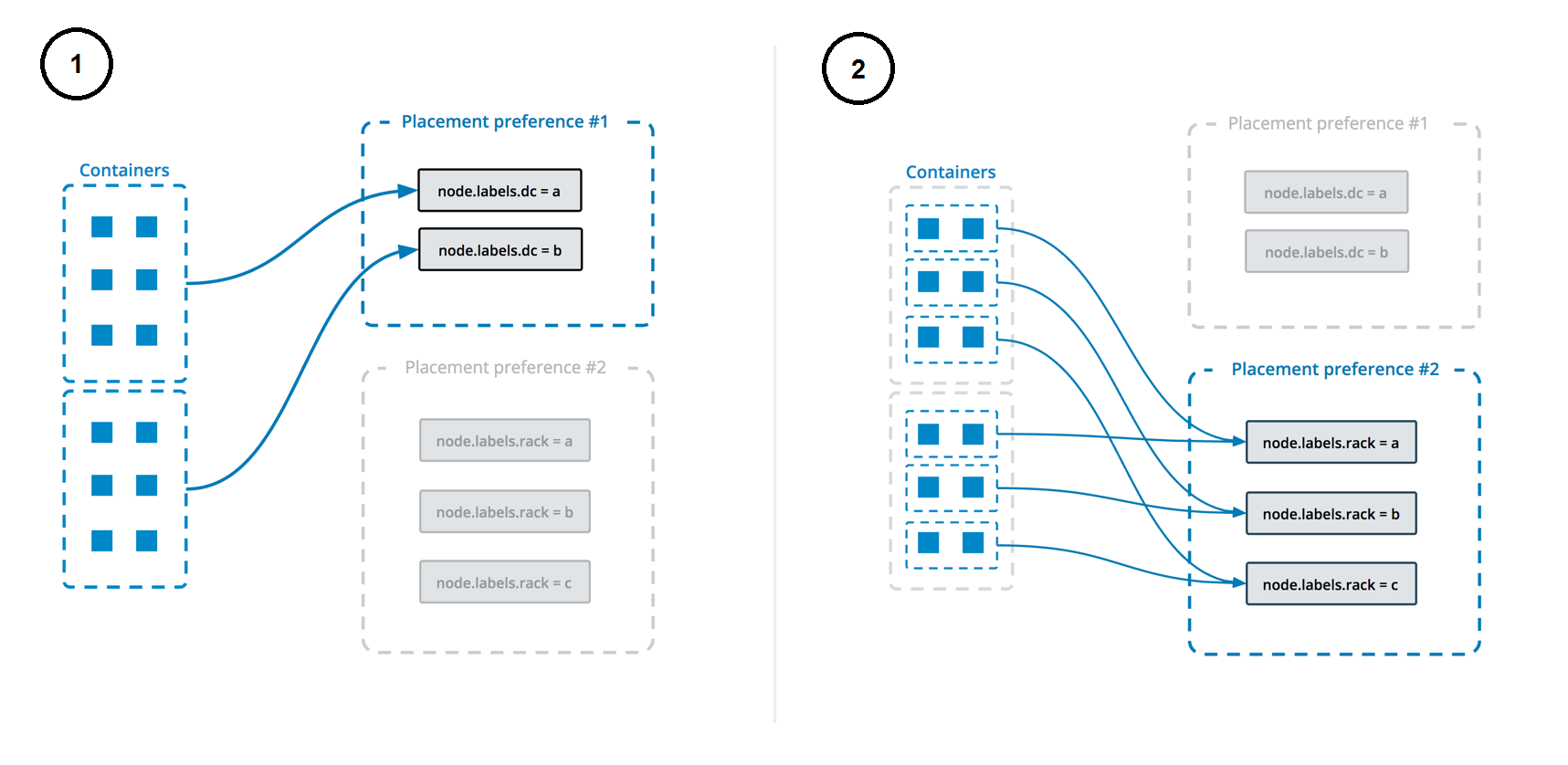
A node.labels.minio label is used to determine which nodes the service can be deployed on.
The deployment uses both placement constraints & preferences to ensure that the servers are spread evenly across the Docker Swarm manager nodes and only ALLOW one replica per node.
See https://docs.docker.com/engine/swarm/services/#control-service-placement for more information.
On the manager node, run the following command to list the nodes in the cluster.
docker node lsOn the manager node, run the following command to add the label to the node.
Repeat this step for each node you want to deploy the service to. Make sure that the number of node updated matches the number of replicas you want to deploy.
Example deploy service with 3 replicas:
docker node update --label-add minio=true <node-1>
docker node update --label-add minio=true <node-2>
docker node update --label-add minio=true <node-3>This stack uses the local driver for the volumes by default. This means that the data will be stored on the local node.
If you want to use a different driver, you need to create a volume name minio-data-1 with the driver you want to use.
Here is an example of creating a volume with the local driver:
# You can specify the driver with the --driver local flag or omit it as it is the default driver.
docker volume create minio-data-1See https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/volume_create/ for more information.
Note
You can add more volumes by adding more minio-data-<n> volumes to the volumes section of the docker-compose.custom.yml file.
If you wish to share data between machines, read here Share data between machines.
Example: Distributed deployment
This is the official diagram from MinIO on how to deploy a distributed environment.
In this example, the SERVER n is the number of nodes you have in your Docker Swarm Cluster (See: Server placement for details on how MinIO deployed to each node).
There are 2 deployment modes for MinIO.
- Single
- Distributed
Before you can deploy MinIO, you need to have a Docker Swarm Cluster up and running with at least 1 or more nodes.
Note
Placements constraints & preferences are used to ensure that only one replica is deployed per node.
See docker-compose.single.yml as an example.
make deploy mode=singleBefore you can deploy MinIO, you need to have a Docker Swarm Cluster up and running with at least 3 or more nodes.
There are some decisions you need to make before deploying MinIO.
- How many MinIO instances do you want to deploy?
- How much storage do you want to allocate to each instance?
Note
Placements constraints & preferences are used to ensure that the servers are spread evenly across the nodes and only one replica is deployed per node.
See docker-compose.distributed.yml as an example.
make deploy
# or
make deploy mode=distributed # (default mode)You can also use the docker-compose.<mode>.yml file to deploy a custom deployment.
Example:
# docker-compose.<mode>.yml
services:
# Deploy 5 MinIO instances
minio:
command: server --console-address ":9001" http://minio-{1...5}:9000/data{1...4}
volumes:
- minio-data-1:/data1
- minio-data-2:/data2
- minio-data-3:/data3
- minio-data-4:/data4
deploy:
replicas: 5
# Deploy 3 ingress instances
ingress:
deploy:
replicas: 3
volumes:
minio-data-1:
minio-data-2:
minio-data-3:
minio-data-4:make deploy mode=custom