In this guide, we will briefly discuss how to add Razorpay as a mode to accept money from users on a React based website. The project stack discussed here is only in JavaScript. Before we proceed, I highly encourage you to watch these two videos to understand how online payment works?
- Demystifying Online Payments - What happens when you make an online purchase and what can go wrong?
- How online payment works
Our goal here is clear and simple, make the payment button of the website functional to accept money from the end-user. Few quick checks have to be taken care of before you proceed:
- An activated account on RazorPay
- Knowledge of JavaScript and React
Once you login to the dashboard, make sure you are on Test mode and NOT in Live mode
The next step is to generate the test API key(s). Navigate to the Settings option onto the left of the screen and click on Generate API keys have the generated values saved onto a side that we will use in the future.
Our react app output is showcasing course cards, whose fundamental action is to trigger a method on node.js backend to activate the payment gateway and collect money from the user's payment source.
Create boiler plate react app code
npx create-react-app lco-payment-gateway
Breaking down from the above image you can say, we have a repeating component Course Card that is populating dynamic information. Create a folder components under src and make a new file CourseCard.js. Accepting props here are
const CourseCard = ({
courseName, courseThumbnail, courseDetails,
coursePrice, courseDiscountedPrice, courseDiscount,
}) => {
return (
<article className="card">
<img src={courseThumbnail} alt={courseName} />
<div className="card-content">
<header className="card-header">
<h5>{courseName}</h5>
</header>
<p>{courseDetails}</p>
<h4>
₹{courseDiscountedPrice}{" "}
<span className="course-price">₹{coursePrice}</span>{" "}
<span className="course-discount-percentage">
{courseDiscount}% OFF
</span>
</h4>
<button
type="button"
className="course-payment-button"
>
Buy Now
</button>
</div>
</article>
);
};
Now import the component onto the home page and pass on the necessary information. (Note: Keeping the tutorial constraint in mind, we are not discussing the CSS here)
const App = () => {
return (
<section className="card-list">
<CourseCard
courseName="Complete React Native
Mobile App developer - Build 10 apps"
courseThumbnail="https://Link to Image"
courseDetails="2 Free + 92 Paid"
coursePrice="2,999"
courseDiscountedPrice="199"
courseDiscount="93"
/>
</section>
);
}
In similar fashion, you can add one or more cards onto home page.
We stand at a point now where the Buy Now button is just a dummy button but doesn't invoke anything related to Razorpay. Now we have to prepare the backend boilerplate code and make a route on visiting the payment gateway logic kicks in.
- Create a new folder named lco-payment-backend and open folder in terminal
- Run
npm init -yand open onto VSCode - Create a new file index.js
- Install dependencies
npm install body-parser cors express nodemon razorpay shortid
- Prepare the imports
const app = require("express")();
const path = require("path");
const cors = require("cors");
const shortid = require("shortid");
const Razorpay = require("razorpay");
const razorpay = new Razorpay({
key_id: "RAZORPAY KEY",
key_secret: "RAZORPAY SECRET",
});
- To avoid CORS errors
app.use(cors());
- Under lco-payment-backend folder paste your brand logo image
app.get("/logo.png", (req, res) => {
res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname, "logo.png"));
});
Information sent from the frontend is generally handled in POST request, our job in the backend is to generate an Order ID and send it back in JSON format to the user to proceed to success or failure screen based on your logic.
- Gather the options(amount, currency)
const payment_capture = 1;
const amount = 499;
const currency = "INR";
const options = {
amount: amount * 100,
currency,
receipt: shortid.generate(),
payment_capture,
};
Always keep the payment information as price and currency handled only on the backend based on the usage from frontend users. Never capture the amount from frontend as there are high chances they will be manipulated by over-smart people. Amount passed has to be multiplied by 100 for Indian rupees. The receipt ID is generated on the fly with help of shortid
- Create an order with the options object and wait for a valid response
app.post("/razorpay", async (req, res) => {
const payment_capture = 1;
const amount = 499;
const currency = "INR";
const options = {
amount: amount * 100,
currency,
receipt: shortid.generate(),
payment_capture,
};
try {
const response = await razorpay.orders.create(options);
console.log(response);
res.json({
id: response.id,
currency: response.currency,
amount: response.amount,
});
} catch (error) {
console.log(error);
}
});
No, we still need to cook the Razorpay sdk onto the react app. The approach here is simple, we are provided with a checkout script from razorpay team that should be loaded on opening the web page. Making use of react hook useEffect we load the script
const loadScript = (src) => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
const script = document.createElement("script");
script.src = src;
script.onload = () => {
resolve(true);
};
script.onerror = () => {
resolve(false);
};
document.body.appendChild(script);
});
};
useEffect(() => {
loadScript("https://checkout.razorpay.com/v1/checkout.js");
});
Loading of this script will open the doors to create that fancy dialog of Razorpay that comes when you click on Buy now button. Again a step back, we are looking at a fundamental object from the Razorpay object as
const paymentObject = new window.Razorpay(options);
paymentObject.open();
A post request has to be made to the /razorpay route that was built in the backend and fetch the information like CURRENCY, AMOUNT, ORDER ID.
The options parameter here is a gaint object that should be holding the information of
- PUBLIC KEY
- CURRENCY
- AMOUNT
- NAME (of the seller)
- DESCRIPTION
- SELLER LOGO
- ORDER ID
- HANDLER (action to perform after getting success/error message from server)
- PREFILL (user information)
const options = {
key: "RAZORPAY PUBLIC KEY",
currency: data.currency,
amount: data.amount,
name: "Learning To Code Online",
description: "Test Wallet Transaction",
image: "http://localhost:1337/logo.png",
order_id: data.id,
handler: function (response) {
alert(response.razorpay_payment_id);
alert(response.razorpay_order_id);
alert(response.razorpay_signature);
},
prefill: {
name: "Anirudh Jwala",
email: "[email protected]",
contact: "9999999999",
},
};
Export this entire method as a functionality to be called on clicking the Buy now button and hook it up to the button
<button
type="button"
onClick={displayRazorpay}
className="course-payment-button">
Buy Now
</button>
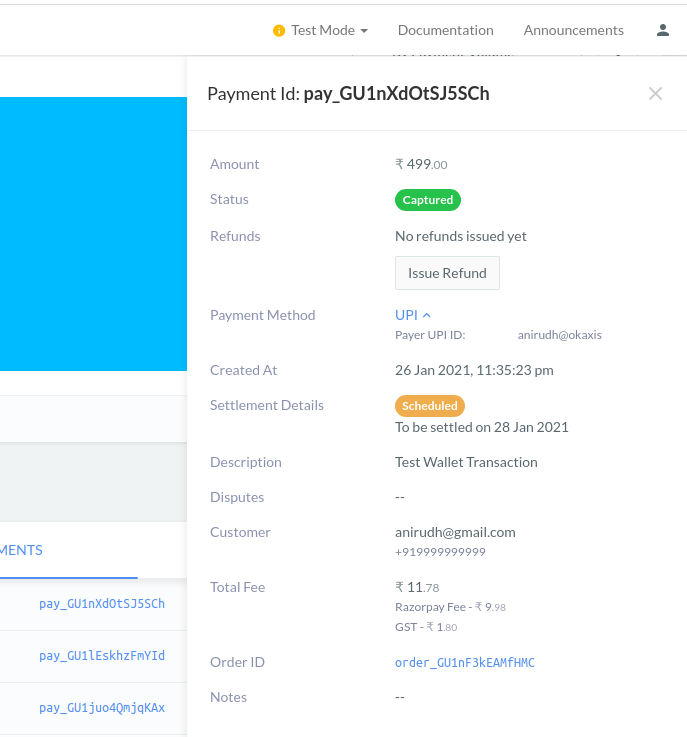
From the demo video as you can see above, we have obtained some information in an alert box, and the same will be available in the razorpay dashboard.Captured money reflects onto your razorpay dashboard
- The payment gateway amount is never decided on the front-end that is the reason in the output we get to see the hardcoded 499 as the amount taken from the backend
- In real-time apps, you have a separate API that serves this information(course amount or product amount) both to the frontend and backend from a single source of truth
- In this demo, we have seen only the test mode, the actual use when you move to LIVE mode the only change in code is the
API keysgenerated from settings of your Razorpay account - Captured money has to be settled by the owner from the Razorpay dashboard to their registered bank account
- If you are following this procedure I highly encourage you to spend at least 1-2 hours on the Razorpay dashboard itself to understand how things are working behind the scenes
- Personalization of payment gateway is available on the dashboard, we can toggle with things like Theme color, brand logo, etc from settings