Table of Contents
The sf-decomposer is a Salesforce CLI plugin that reads the original metadata files (XML) and creates smaller, more manageable files for version control. The inverse function (recompose) will recreate deployment-compatible metadata files. This plugin is intended for users who deploy their Salesforce codebase from any repository that follows the Salesforce DX Project Configuration (sfdx-project.json file), not just git-based ones.
This will parse and retain the following in the original XMLs:
- Character Data (CDATA)
- Comments
- Attributes
The decomposed file format can be XML, JSON, or YAML. Based on testing, XML and YAML handle CDATA formatting more nicely than JSON.
DISCLAIMERS:
- You must update the
.forceignoreto have the Salesforce CLI ignore the decomposed files created by this plugin. See sectionIgnore Files.- Updates to the
.gitignoreare optional if you are using this in a git-based repo and can be updated based on what you want to be staged in your repo.
- Updates to the
- It is recommended that you extensively test this plugin in a sandbox environment on the metadata types for which you wish to use this tool.
- Do not change your production/QA pipelines until you have tested this and are happy with the results.
- Ensure your deployment pipelines are stable before implementing this plugin.
sf plugins install [email protected]Why should you consider using this Salesforce CLI Plugin over Salesforce's decomposition:
- Salesforce's decomposition betas are evaluated for each metadata type before they are considered. My plugin already supports the vast majority of Salesforce metadata types available from the Metadata API.
- Salesforce's decomposition is all or nothing for each metadata type. Meaning, if you want to decompose workflows, all of your workflows will need to be decomposed to work with Salesforce's approach. My plugin allows you to selectively decompose for each metadata type.
- Some metadata types may only be partially decomposed by Salesforce such as permission sets based on what designs are picked. My plugin will allow for total decomposition. So if a user wants to fully decompose permission sets, they can use this plugin.
The sf-decomposer supports 2 commands:
sf decomposer decomposesf decomposer recompose
Both commands need to be run somewhere inside your Salesforce DX repository (root folder is preferred). This plugin will look for the sfdx-project.json file in the root folder and process all package directories listed in the file.
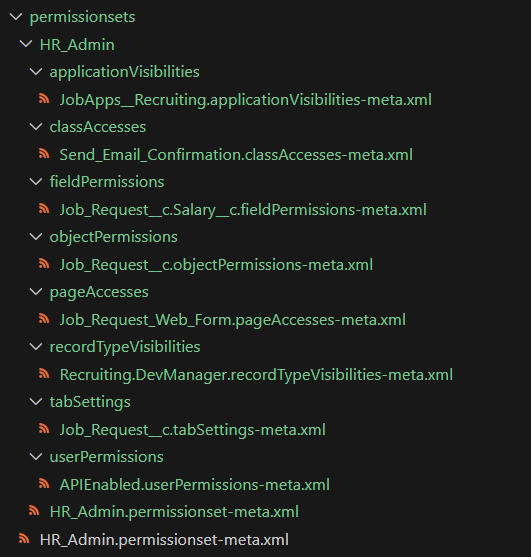
Decomposes the original metadata files into smaller files for version control. Except for custom labels, the smaller files will be placed into new sub-directories:
Custom labels will be decomposed directly in the root labels folder:
Unique ID elements are used to name decomposed files for nested elements. The default unique ID elements for all metadata types are <fullName> and <name>. In this example XML below, the <fullName> tag is included in the nested element and its contents (quoteAuto) will be used to name the decomposed file.
<labels>
<fullName>quoteAuto</fullName>
<value>This is an automatically generated quote.</value>
<language>en_US</language>
<protected>false</protected>
<shortDescription>Automatic Quote</shortDescription>
</labels>If the default unique ID elements are not found in the nested element, the plugin will look for any other metadata-specific unique ID elements (see the Contributing section for more information). If a unique ID element is not found, the short SHA-256 hash of the element contents will be used to name the decomposed file, as shown below. It's recommended to add the --prepurge flag to the decompose command to remove pre-existing decomposed files that may conflict with newer decomposed files due to different SHA hashes.
Using the --format flag, you can set the desired file type for the decomposed files to XML (default), YAML, or JSON.
Note: The --format flag for the recompose command must match what you selected for the decompose --format.
USAGE
$ sf decomposer decompose -m <value> -f <value> [--prepurge --postpurge --debug --json]
FLAGS
-m, --metadata-type=<value> The metadata suffix to process, such as 'flow', 'labels', etc. You can provide this flag multiple times to process multiple metadata types with a single command.
-f, --format=<value> [default: 'xml'] The file type for the decomposed files.
--prepurge [default: false] If provided, purge directories of pre-existing decomposed files.
--postpurge [default: false] If provided, purge the original files after decomposing them.
--debug [default: false] If provided, log debugging results to a text file (disassemble.log).
GLOBAL FLAGS
--json Format output as json.
DESCRIPTION
This command will read all of the original metadata files and separate them into smaller files in each package directory.
These smaller decomposed files can be XMLs, YAMLs, or JSONs.
You should run this after you retrieve metadata from an org.
EXAMPLES
Decompose all flows:
$ sf decomposer decompose -m "flow" -f "xml" --prepurge --postpurge --debug
Decompose all flows and custom labels:
$ sf decomposer decompose -m "flow" -m "labels" -f "xml" --prepurge --postpurge --debug
Reads the files created by the decompose command and recreates deployment-compatible metadata files.
Ensure the --format flag of the recompose command matches the file format selected for the --format flag in the decompose command. File formats for the decomposed files can be XML (default), YAML, or JSON.
This command will always create XMLs as its output format.
USAGE
$ sf decomposer recompose -m <value> -f <value> [--postpurge --debug --json]
FLAGS
-m, --metadata-type=<value> The metadata suffix to process, such as 'flow', 'labels', etc. You can provide this flag multiple times to process multiple metadata types with a single command.
-f, --format=<value> [default: 'xml'] The file format for the decomposed files.
--postpurge [default: false] If provided, purge the decomposed files after recomposing them.
--debug [default: false] If provided, log debugging results to a text file (disassemble.log).
GLOBAL FLAGS
--json Format output as json.
DESCRIPTION
This command will read the decomposed files and recreate deployment-compatible metadata files in each package directory.
You should run this before you deploy decomposed metadata to an org.
EXAMPLES
Recompose all flows:
$ sf decomposer recompose -m "flow" -f "xml" --postpurge --debug
Recompose all flows and custom labels:
$ sf decomposer recompose -m "flow" -m "labels" -f "xml" --postpurge --debug
All parent metadata types imported from this plugin's version of @salesforce/source-deploy-retrieve (SDR) toolkit are supported except for certain types.
The --metadata-type/-m flag should be the metadata's "suffix" value as listed in the metadataRegistry.json.
The suffix is this part of the original meta file name - labels is the suffix in *.labels-meta.xml.
Here are some examples:
- Custom Labels (
--metadata-type "labels") - Workflows (
--metadata-type "workflow") - Profiles (
--metadata-type "profile") - Permission Sets (
--metadata-type "permissionset") - Flows (
--metadata-type "flow") - Matching Rules (
--metadata-type "matchingRule") - Assignment Rules (
--metadata-type "assignmentRules") - Escalation Rules (
--metadata-type "escalationRules") - Sharing Rules (
--metadata-type "sharingRules") - Auto Response Rules (
--metadata-type "autoResponseRules") - Global Value Set Translation (
--metadata-type "globalValueSetTranslation") - Standard Value Set Translation (
--metadata-type "standardValueSetTranslation") - Translations (
--metadata-type "translation") - Standard Value Sets (
--metadata-type "standardValueSet") - Global Value Sets (
--metadata-type "globalValueSet") - AI Scoring Model Definition (
--metadata-type "aiScoringModelDefinition") - Decision Matrix Definition (
--metadata-type "decisionMatrixDefinition") - Bot (
--metadata-type "bot")- NOTE: Running "bot" will also decompose and recompose Bot Version meta files
- The
botVersionmeta suffix will be blocked from running directly
- Marketing App Extension (
--metadata-type "marketingappextension")
botVersion is blocked from being ran directly. Please use the bot meta suffix to decompose and recompose bots and bot versions.
Error (1): `botVersion` suffix should not be used. Please use `bot` to decompose/recompose bot and bot version files.
Custom Objects are not supported by this plugin.
Error (1): Custom Objects are not supported by this plugin.
Metadata types such as Apex Classes, Apex Components, Triggers, etc. with certain SDR adapter strategies (matchingContentFile, digitalExperience, mixedContent, bundle) are not supported by this plugin.
Error (1): Metadata types with [matchingContentFile, digitalExperience, mixedContent, bundle] strategies are not supported by this plugin.
Children metadata types (ex: custom fields) are not supported and will result in this general error:
Error (1): Metadata type not found for the given suffix: field.
The plugin searches the current working directory for the sfdx-project.json, and if it's not found in the current working directory, it will search upwards for it until it hits your root drive. If the sfdx-project.json file isn't found, the plugin will fail with:
Error (1): sfdx-project.json not found in any parent directory.
The package used to decompose and recompose XMLs, xml-disassembler, will log errors, and optionally debugging statements, to a log file, disassemble.log. This log will be created in the working directory and will be created when running this plugin at all times. If there were no XML decomposing/recomposing errors, this log will simply be empty.
By default, this package will only log errors to the file. This plugin will print xml-disassembler errors as warnings in the command terminal to allow all other files to be processed.
These warnings when running decompose and recompose commands will look as such:
Warning: C:\Users\matth\Documents\sf-decomposer\test\baselines\flows\Get_Info\actionCalls\Get_Info.actionCalls-meta.xml was unabled to be parsed and will not be processed. Confirm formatting and try again.
To add additional debugging statements to the log file, provide the --debug flag to either command to generate additional logging statements to disassemble.log.
General debugging statements in the log file will look like:
[2024-03-30T14:28:37.959] [DEBUG] default - Created disassembled file: mock\no-nested-elements\HR_Admin\HR_Admin.permissionset-meta.xml
Recommend adding the disassemble.log to your .gitignore file if you are using this in a git-based repo.
If you wish, you can create an ignore file in the root of your repository named .sfdecomposerignore to ignore specific XMLs when running the decompose command.
The ignore file should follow .gitignore spec 2.22.1.
When the decompose command is ran with the --debug flag and it processes a file that matches an entry in .sfdecomposerignore, a warning will be printed to the disassemble.log:
[2024-05-22T09:32:12.078] [WARN] default - File ignored by .sfdecomposerignore: C:\Users\matth\Documents\sf-decomposer\test\baselines\bots\Assessment_Bot\v1.botVersion-meta.xml
The ignore file is not read by the recompose command.
A post-retrieve hook (for the decompose command) and a pre-run hook (for the recompose command) have been configured if you elect to use them.
The post-retrieve hook will automatically decompose the desired metadata types after every Salesforce CLI retrieval (sf project retrieve start command).
The pre-run hook will automatically recompose the desired metadata types before every Salesforce CLI deployment/validation (sf project deploy start and sf project deploy validate commands).
Both hooks require you to create this file in the root of your repo: .sfdecomposer.config.json
The .sfdecomposer.config.json should look like this:
{
"metadataSuffixes": "labels,workflow,profile",
"prePurge": true,
"postPurge": true,
"decomposedFormat": "xml"
}metadataSuffixesis required and should be a comma-separated string of metadata suffixes to decompose automatically after retrievals.prePurgeis optional and should be a boolean. If true, this will delete any existing decomposed files before decomposing the files. If you do not provide this, the default will befalse. This flag is not used by the recompose command/pre-run hook.postPurgeis optional and should be a boolean. If true, this will delete the retrieval file after decomposing it or delete the decomposed files after recomposing them. If you do not provide this, the default will befalse.decomposedFormatis optional and should be eitherxml,json, oryaml, depending on what file format you want the decomposed files created as. If you do not provide this, the default will bexml.
If the .sfdecomposer.config.json file isn't found, the hooks will be skipped.
NOTE: In order to avoid errors during the retrieval, you must configure your .forceignore file to have the Salesforce CLI ignore the decomposed files. See section below.
You must update the .forceignore to have the Salesforce CLI ignore the decomposed files created by this plugin. Optionally, you can add the recomposed files to your .gitignore to avoid staging those in your git-based repository.
The Salesforce CLI should ignore the decomposed files and should allow the recomposed files. Update based on the decomposed file format you are using (.xml, .json, or .yaml).
# Ignore decomposed files
**/profiles/**/*.xml
**/permissionsets/**/*.xml
**/labels/*.xml
**/workflows/**/*.xml
**/flows/**/*.xml
**/matchingRules/**/*.xml
**/assignmentRules/**/*.xml
**/escalationRules/**/*.xml
**/sharingRules/**/*.xml
**/autoResponseRules/**/*.xml
**/globalValueSetTranslations/**/*.xml
**/standardValueSetTranslations/**/*.xml
**/translations/**/*.xml
**/globalValueSets/**/*.xml
**/standardValueSets/**/*.xml
**/decisionMatrixDefinition/**/*.xml
**/aiScoringModelDefinitions/**/*.xml
**/bots/**/*.xml
**/marketingappextensions/**/*.xml
# Allow the recomposed files
!**/permissionsets/*.permissionset-meta.xml
!**/labels/CustomLabels.labels-meta.xml
!**/workflows/*.workflow-meta.xml
!**/profiles/*.profile-meta.xml
!**/flows/*.flow-meta.xml
!**/matchingRules/*.matchingRule-meta.xml
!**/assignmentRules/*.assignmentRules-meta.xml
!**/escalationRules/*.escalationRules-meta.xml
!**/sharingRules/*.sharingRules-meta.xml
!**/autoResponseRules/*.autoResponseRules-meta.xml
!**/globalValueSetTranslations/*.globalValueSetTranslation-meta.xml
!**/standardValueSetTranslations/*.standardValueSetTranslation-meta.xml
!**/translations/*.translation-meta.xml
!**/globalValueSets/*.globalValueSet-meta.xml
!**/standardValueSets/*.standardValueSet-meta.xml
!**/decisionMatrixDefinition/*.decisionMatrixDefinition-meta.xml
!**/aiScoringModelDefinitions/*.aiScoringModelDefinition-meta.xml
!**/bots/*/*.botVersion-meta.xml
!**/bots/*/*.bot-meta.xml
!**/marketingappextensions/*.marketingappextension-meta.xml
I recommend having Git (or whatever version control system you are using) ignore the recomposed files so you don't stage those in your repositories.
# Ignore recomposed files
**/permissionsets/*.permissionset-meta.xml
**/profiles/*.profile-meta.xml
**/labels/CustomLabels.labels-meta.xml
**/workflows/*.workflow-meta.xml
**/flows/*.flow-meta.xml
**/matchingRules/*.matchingRule-meta.xml
**/assignmentRules/*.assignmentRules-meta.xml
**/escalationRules/*.escalationRules-meta.xml
**/sharingRules/*.sharingRules-meta.xml
**/autoResponseRules/*.autoResponseRules-meta.xml
**/globalValueSetTranslations/*.globalValueSetTranslation-meta.xml
**/standardValueSetTranslations/*.standardValueSetTranslation-meta.xml
**/translations/*.translation-meta.xml
**/globalValueSets/*.globalValueSet-meta.xml
**/standardValueSets/*.standardValueSet-meta.xml
**/decisionMatrixDefinition/*.decisionMatrixDefinition-meta.xml
**/aiScoringModelDefinitions/*.aiScoringModelDefinition-meta.xml
**/bots/*/*.botVersion-meta.xml
**/bots/*/*.bot-meta.xml
**/marketingappextensions/*.marketingappextension-meta.xml
Your VCS should also ignore the log created by the xml-disassembler package.
disassemble.log
Contributions are welcome! If you would like to contribute, please fork the repository, make your changes, and submit a pull request.
To add more unique ID elements for a metadata type, you can update the src/metadata/uniqueIdElements.json file. The metadata type's suffix should be used as the key.
If you encounter any issues, please create an issue in the repository's issue tracker. Please also create issues for feature enhancements or to support newer metadata types added to the SDR toolkit.
This project is licensed under the MIT license. Please see the LICENSE file for details.