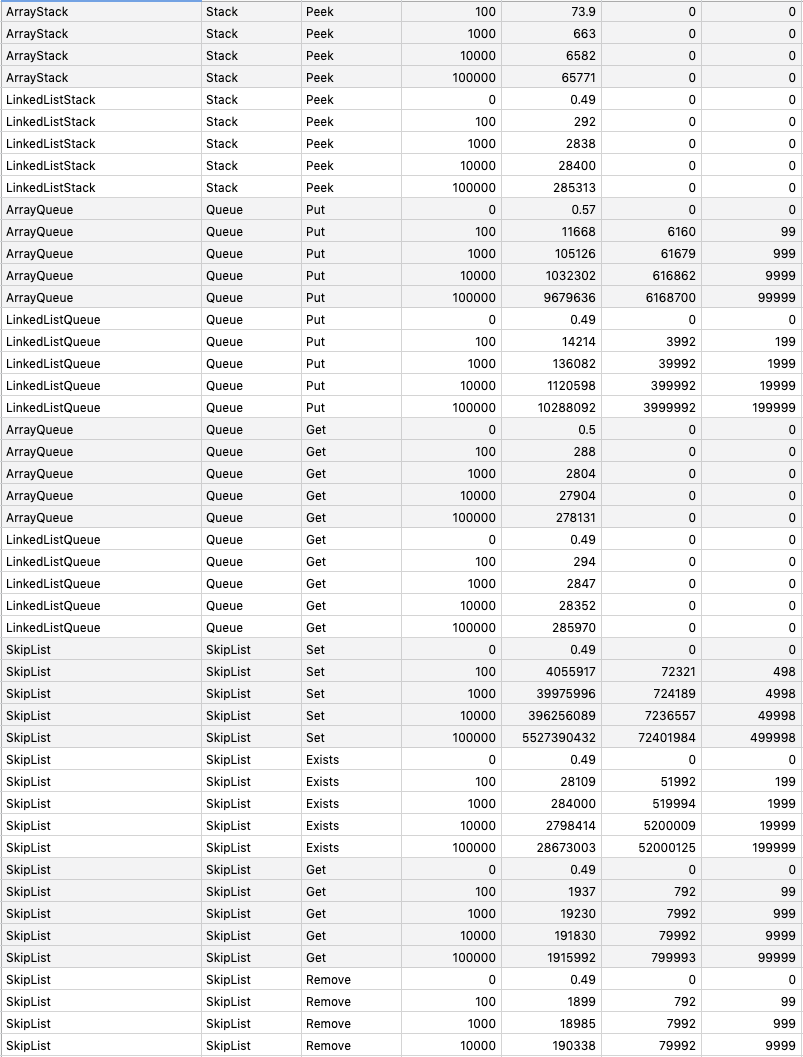
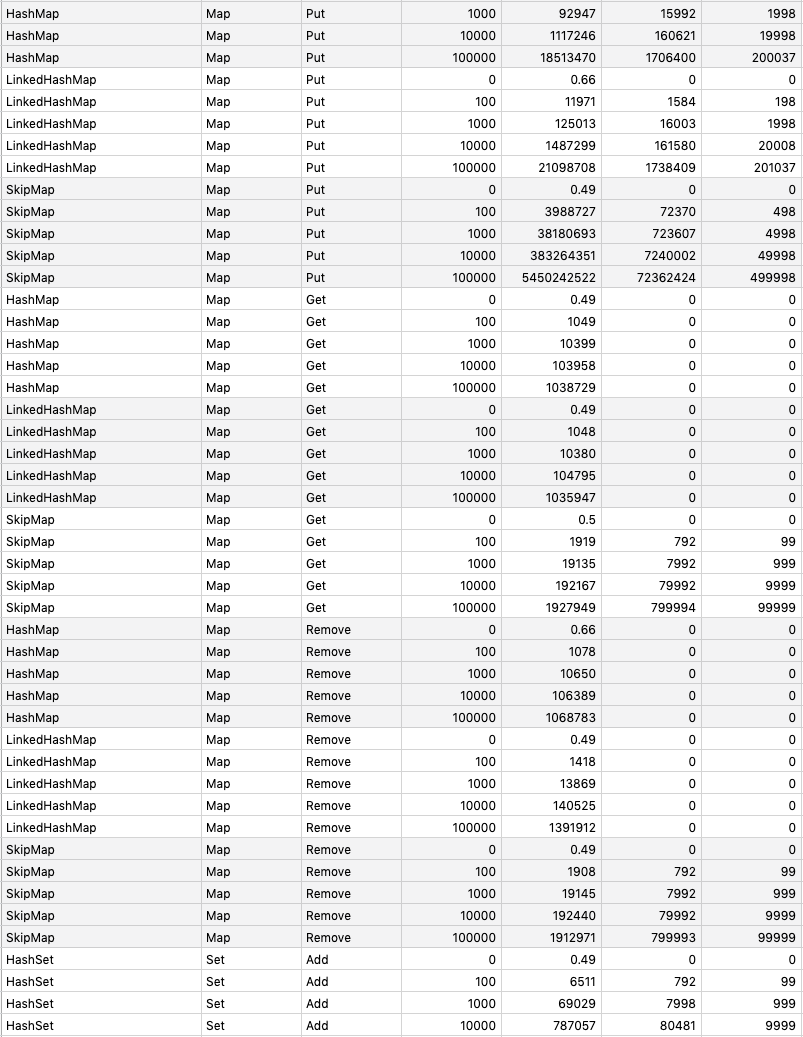
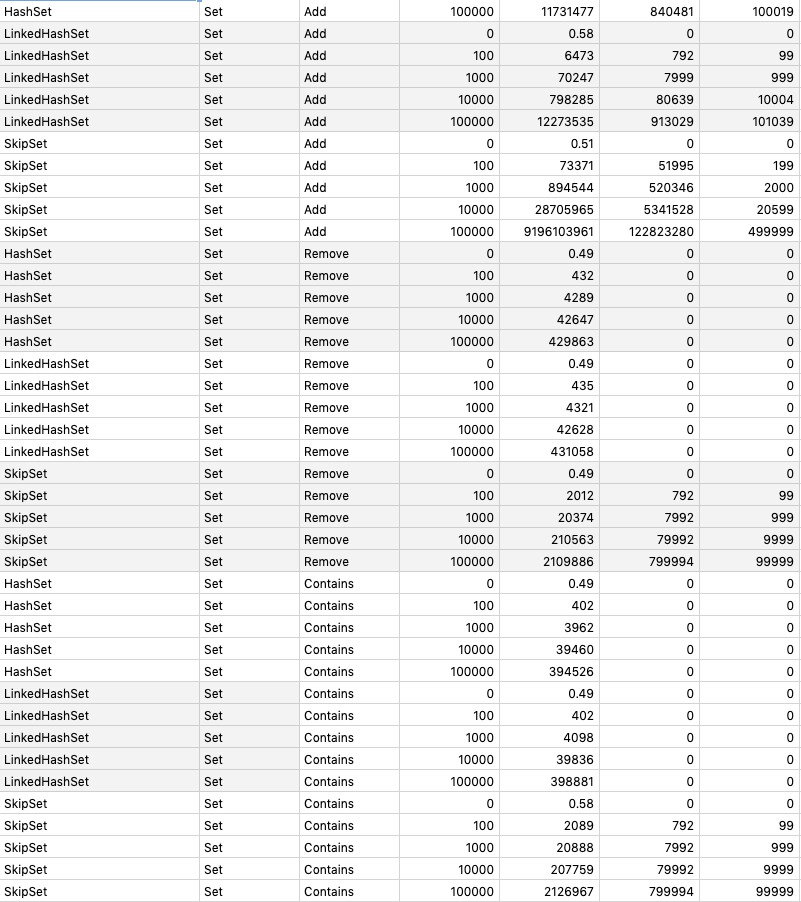
Implement data structures with Go.
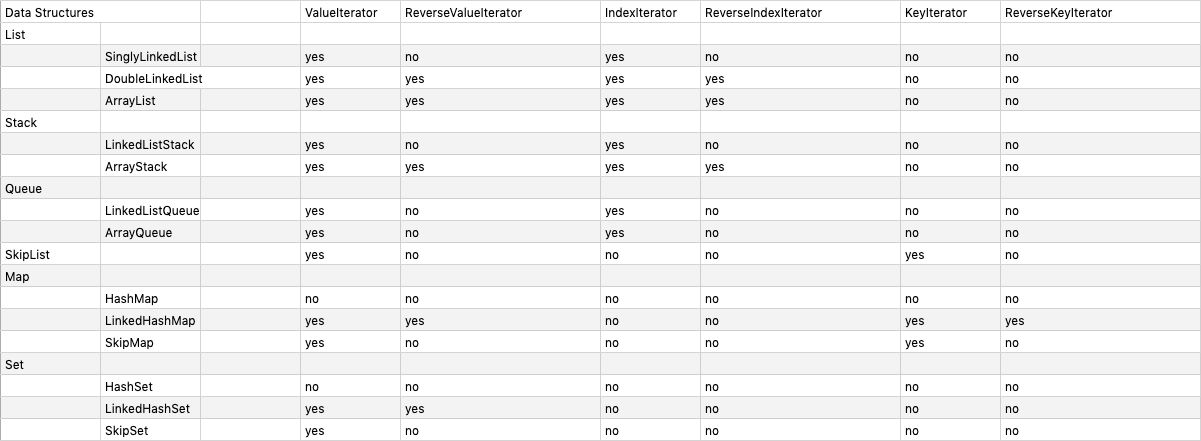
The package provides six iterators as following.
ValueIterator traverses the value backward.
type ValueIterator interface {
Next() bool
Begin()
Value() interface{}
}ReverseValueIterator can traverse values forward or backward.
type ReverseValueIterator interface {
ValueIterator
Prev() bool
End()
}IndexIterator traverses the index-value pair backward.
type IndexIterator interface {
ValueIterator
Index() int
}ReverseIndexIterator can traverse the index-value pair forward or backward.
type ReverseIndexIterator interface {
IndexIterator
Prev() bool
End()
}KeyIterator traverses the key-value pair backward.
type KeyIterator interface {
ValueIterator
Key() interface{}
}ReverseKeyIterator can traverse the key-value pair forward or backward.
type ReverseKeyIterator interface {
KeyIterator
Prev() bool
End()
}Different data structures have different support for iterator as following.
All data structures will implement the Container interface.
type Container interface {
Empty() bool
Size() int
Clear()
Values() []interface{}
}List is ordered and value repeatable.
Implements Container interface.
type List interface {
Append(values ...interface{})
Get(index int) (interface{}, error)
Remove(index int) error
Contains(values ...interface{}) bool
Swap(i, j int) error
Insert(index int, values ...interface{}) error
Set(index int, value interface{}) error
IndexOf(value interface{}) (int, error)
container.Container
// Empty() bool
// Size() int
// Clear()
// Values() []interface{}
}The current element of SinglyLinkedList points to the next element.
Implements List, ValueIterator and IndexIterator interface.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/list/singlylinkedlist"
)
func main() {
list := singlylinkedlist.New() // []
list.Append(1) // [1]
list.Append(2) // [1, 2]
list.Append(3) // [1, 2, 3]
list.PreAppend(4) // [4, 1, 2, 3]
_, _ = list.Get(0) // 4, nil
_, _ = list.Get(999) // nil, ErrIndex
_ = list.Remove(2) // [4, 1, 3]
_ = list.Contains() // true
_ = list.Contains(4, 1) // true
_ = list.Contains(4, 3) // true
_ = list.Contains(4, 1, 3, 5) // false
_ = list.Swap(0, 1) // [1, 4, 3]
_ = list.Insert(1, 5, 6, 7, 8) // [1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 3]
_ = list.Set(3, -1) // [1, 4, 5, -1, 7, 8, 3]
// iterator
it := list.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Index(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 0 1
// 1 4
// 2 5
// 3 -1
// 4 7
// 5 8
// 6 3
_, _ = list.IndexOf(1) // 0, nil
_, _ = list.IndexOf(8) // 5, nil
_, _ = list.IndexOf(100) // -1, ErrIndexOf
list.Reverse() // [3, 8, 7, -1, 5, 4, 1]
_ = list.Empty() // false
_ = list.Size() // 7
_ = list.Values() // [3 8 7 -1 5 4 1]
list.Clear() // []
}The current and next elements of the DoubleLinkedList point to each other.
Implements List, ValueIterator, ReverseValueIterator, IndexIterator and ReverseIndexIterator interface.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/list/doublelinkedlist"
)
func main() {
list := doublelinkedlist.New() // []
list.Append(1) // [1]
list.Append(2) // [1 2]
list.Append(3) // [1 2 3]
list.PreAppend(4) // [4 1 2 3]
_, _ = list.Get(0) // 4, nil
_, _ = list.Get(999) // nil, ErrIndex
_ = list.Remove(2) // [4 1 3]
_ = list.Contains() // true
_ = list.Contains(4, 1) // true
_ = list.Contains(4, 3) // true
_ = list.Contains(4, 1, 3, 5) // false
_ = list.Swap(0, 1) // [1 4 3]
_ = list.Insert(1, 5, 6, 7, 8) // [1 4 5 6 7 8 3]
_ = list.Set(3, -1) // [1 4 5 -1 7 8 3]
// iterator
it := list.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Index(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 0 1
// 1 4
// 2 5
// 3 -1
// 4 7
// 5 8
// 6 3
it.End()
for it.Prev() {
fmt.Println(it.Index(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 6 3
// 5 8
// 4 7
// 3 -1
// 2 5
// 1 4
// 0 1
_, _ = list.IndexOf(1) // 0, nil
_, _ = list.IndexOf(8) // 5, nil
_, _ = list.IndexOf(100) // -1, ErrIndexOf
list.Reverse() // [3 8 7 -1 5 4 1]
_ = list.Empty() // false
_ = list.Size() // 7
_ = list.Values() // [3 8 7 -1 5 4 1]
list.Clear() // []
}ArrayList is a dynamic array that can be dynamically scaled based on capacity and number of elements.
Implements List, ValueIterator, ReverseValueIterator, IndexIterator and ReverseIndexIterator interface.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/list/arraylist"
)
func main() {
list := arraylist.New() // []
list.Append(1) // [1]
list.Append(2) // [1 2]
list.Append(3) // [1 2 3]
_, _ = list.Get(0) // 1, nil
_, _ = list.Get(999) // nil, ErrIndex
_ = list.Remove(2) // [1 2]
_ = list.Contains() // true
_ = list.Contains(1, 2) // true
_ = list.Contains(2) // true
_ = list.Contains(1, 2, 3) // false
_ = list.Swap(0, 1) // [2 1]
_ = list.Insert(1, 5, 6, 7, 8) // [2 1 5 6 7 8]
_ = list.Set(3, -1) // [2 1 5 -1 7 8]
// iterator
it := list.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Index(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 0 2
// 1 1
// 2 5
// 3 -1
// 4 7
// 5 8
it.End()
for it.Prev() {
fmt.Println(it.Index(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 5 8
// 4 7
// 3 -1
// 2 5
// 1 1
// 0 2
_, _ = list.IndexOf(1) // 1, nil
_, _ = list.IndexOf(8) // 5, nil
_, _ = list.IndexOf(100) // -1, ErrIndexOf
_ = list.Empty() // false
_ = list.Size() // 6
_ = list.Values() // [2 1 5 -1 7 8]
list.Clear() // []
}Stack is a FILO data structure.
Implements Container interface.
type Stack interface {
Push(value interface{})
Pop() (interface{}, error)
Peek() (interface{}, error)
container.Container
// Empty() bool
// Size() int
// Clear()
// Values() []interface{}
}LinkedListStack is a stack based on SinglyLinkedList.
Implements Stack, ValueIterator and IndexIterator interface.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/stack/linkedliststack"
)
func main() {
stack := linkedliststack.New() // []
stack.Push(1) // [1]
stack.Push(2) // [2 1]
stack.Push(3) // [3 2 1]
// iterator
it := stack.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Index(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 0 3
// 1 2
// 2 1
_, _ = stack.Peek() // 3, nil
_, _ = stack.Pop() // 3, nil
_, _ = stack.Peek() // 2, nil
_ = stack.Empty() // false
_ = stack.Size() // 2
_ = stack.Values() // [2 1]
stack.Clear() // []
}ArrayStack is a stack based on ArrayList.
Implements Stack, ValueIterator, ReverseValueIterator, IndexIterator and ReverseIndexIterator interface.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/stack/arraystack"
)
func main() {
stack := arraystack.New() // []
stack.Push(1) // [1]
stack.Push(2) // [2 1]
stack.Push(3) // [3 2 1]
// iterator
it := stack.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Index(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 0 3
// 1 2
// 2 1
_, _ = stack.Peek() // 3, nil
_, _ = stack.Pop() // 3, nil
_, _ = stack.Peek() // 2, nil
_ = stack.Empty() // false
_ = stack.Size() // 2
_ = stack.Values() // [2 1]
stack.Clear() // []
}Queue is a FIFO data structure.
Implements Container interface.
type Queue interface {
Put(value interface{})
Get() (interface{}, error)
container.Container
// Empty() bool
// Size() int
// Clear()
// Values() []interface{}
}LinkedListQueue is a stack based on SinglyLinkedList.
Implements Queue, ValueIterator and IndexIterator interface.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/queue/linkedlistqueue"
)
func main() {
queue := linkedlistqueue.New() // []
queue.Put(1) // [1]
queue.Put(2) // [1 2]
queue.Put(3) // [1 2 3]
queue.Put(4) // [1 2 3 4]
// iterator
it := queue.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Index(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 0 1
// 1 2
// 2 3
// 3 4
_, _ = queue.Get() // 1, nil
_, _ = queue.Get() // 2, nil
_ = queue.Empty() // false
_ = queue.Size() // 2
_ = queue.Values() // [3 4]
queue.Clear() // []
}ArrayQueue is a stack based on ArrayList.
Implements Queue, ValueIterator and IndexIterator interface.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/queue/arrayqueue"
)
func main() {
queue := arrayqueue.New() // []
queue.Put(1) // [1]
queue.Put(2) // [1 2]
queue.Put(3) // [1 2 3]
queue.Put(4) // [1 2 3 4]
// iterator
it := queue.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Index(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 0 1
// 1 2
// 2 3
// 3 4
_, _ = queue.Get() // 1, nil
_, _ = queue.Get() // 2, nil
_ = queue.Empty() // false
_ = queue.Size() // 2
_ = queue.Values() // [3 4]
queue.Clear() // []
}SkipList is a random data structure with performance comparable to that of red-black trees. It should be noted that the keys must be comparable types and element will be sorted by keys.
Implements Container, ValueIterator and KeyIterator interface.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/skiplist"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/util"
)
func main() {
skiplist := skiplist.New(util.IntComparator) // []
skiplist.Set(1, "a") // [{1: "a"}]
skiplist.Set(2, "b") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"}]
skiplist.Set(3, "c") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"} {3: "c"}]
skiplist.Set(4, "d") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"} {3: "c"} {4: "d"}]
// iterator
it := skiplist.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Key(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 1 a
// 2 b
// 3 c
// 4 d
_ = skiplist.Exists(1) // true
_ = skiplist.Exists(9) // false
_, _ = skiplist.Get(1) // "a", nil
_, _ = skiplist.Get(3) // "c", nil
_ = skiplist.Remove(2) // nil
_ = skiplist.Keys() // [1 3 4]
_ = skiplist.Empty() // false
_ = skiplist.Size() // 3
_ = skiplist.Values() // [a c d]
skiplist.Clear() // []
}Map stores key-value pairs with excellent operational performance. It should be noted that the keys must be comparable types.
Implements Container interface.
type Map interface {
Put(key, value interface{})
Get(key interface{}) (interface{}, error)
Remove(key interface{})
container.Container
// Empty() bool
// Size() int
// Clear()
// Values() []interface{}
}HashMap is a map based on hash table.
Implements Map interface.
package main
import (
"github.com/prprprus/ds/maps/hashmap"
)
func main() {
m := hashmap.New() // []
m.Put(1, "a") // [{1: "a"}]
m.Put(2, "b") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"}]
m.Put(3, "c") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"} {3: "c"}]
m.Put(4, "d") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"} {3: "c"} {4: "d"}]
_ = m.Keys() // [1 2 3 4] (Note: order of random)
_, _ = m.Get(1) // "a", nil
_, _ = m.Get(3) // "c", nil
_ = m.Remove(2) // nil
_ = m.Keys() // [1 3 4]
_ = m.Empty() // false
_ = m.Size() // 3
_ = m.Values() // [a c d] (Note: order of random)
m.Clear() // []
}LinkedHashMap is a map based on hash table and DoubleLinkedList, it provides ordered key-value pairs.
Implements Map, ValueIterator, ReverseValueIterator, KeyIterator and ReverseKeyIterator interface.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/maps/linkedhashmap"
)
func main() {
m := linkedhashmap.New() // []
m.Put(1, "a") // [{1: "a"}]
m.Put(2, "b") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"}]
m.Put(3, "c") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"} {3: "c"}]
m.Put(4, "d") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"} {3: "c"} {4: "d"}]
// iterator
it := m.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Key(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 1 a
// 2 b
// 3 c
// 4 d
it.End()
for it.Prev() {
fmt.Println(it.Key(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 4 d
// 3 c
// 2 b
// 1 a
_ = m.Keys() // [1 2 3 4]
_, _ = m.Get(1) // "a", nil
_, _ = m.Get(3) // "c", nil
_ = m.Remove(2) // nil
_ = m.Keys() // [1 3 4]
_ = m.Empty() // false
_ = m.Size() // 3
_ = m.Values() // [a c d]
m.Clear() // []
}SkipMap is a map based on SkipList.
Implements Map, ValueIterator and KeyIterator.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/maps/linkedhashmap"
)
func main() {
m := linkedhashmap.New() // []
m.Put(1, "a") // [{1: "a"}]
m.Put(2, "b") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"}]
m.Put(3, "c") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"} {3: "c"}]
m.Put(4, "d") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"} {3: "c"} {4: "d"}]
// iterator
it := m.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Key(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 1 a
// 2 b
// 3 c
// 4 d
_ = m.Keys() // [1 2 3 4]
_, _ = m.Get(1) // "a", nil
_, _ = m.Get(3) // "c", nil
_ = m.Remove(2) // nil
_ = m.Keys() // [1 3 4]
_ = m.Empty() // false
_ = m.Size() // 3
_ = m.Values() // [a c d]
m.Clear() // []
}Set is used to store non-repeating values, usually with good operational performance.
Implements Container interface.
type Set interface {
Add(values ...interface{})
Remove(values ...interface{}) error
Contains(values ...interface{}) bool
container.Container
// Empty() bool
// Size() int
// Clear()
// Values() []interface{}
}HashSet is a set based on hash table.
Implements Set interface.
package main
import (
"github.com/prprprus/ds/set/hashset"
)
func main() {
s := hashset.New() // []
s.Add(1) // [1]
s.Add(2) // [1 2]
s.Add(3) // [1 2 3]
_ = s.Contains() // true
_ = s.Contains(1, 2, 3) // true
_ = s.Contains(1, 3) // true
_ = s.Contains(2, 3, 4) // false
_ = s.Remove(2) // nil
_ = s.Empty() // false
_ = s.Size() // 2
_ = s.Values() // [1 3]
s.Clear() // []
}LinkedHashSet is a set based on hash table and DoubleLinkedList, it provides ordered value.
Implements Set, ValueIterator and ReverseValueIterator interface.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/set/linkedhashset"
)
func main() {
s := linkedhashset.New() // []
s.Add(1) // [1]
s.Add(2) // [1 2]
s.Add(3) // [1 2 3]
// iterator
it := s.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Value())
}
// output:
// 1
// 2
// 3
it.End()
for it.Prev() {
fmt.Println(it.Value())
}
// output:
// 3
// 2
// 1
_ = s.Contains() // true
_ = s.Contains(1, 2, 3) // true
_ = s.Contains(1, 3) // true
_ = s.Contains(2, 3, 4) // false
_ = s.Remove(2) // nil
_ = s.Empty() // false
_ = s.Size() // 2
_ = s.Values() // [1 3]
s.Clear() // []
}SkipSet is a set based on SkipList.
Implements Set and ValueIterator interface.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/set/skipset"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/util"
)
func main() {
s := skipset.New(util.IntComparator) // []
s.Add(1) // [1]
s.Add(2) // [1 2]
s.Add(3) // [1 2 3]
// iterator
it := s.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Value())
}
// output:
// 1
// 2
// 3
_ = s.Contains() // true
_ = s.Contains(1, 2, 3) // true
_ = s.Contains(1, 3) // true
_ = s.Contains(2, 3, 4) // false
_ = s.Remove(2) // nil
_ = s.Empty() // false
_ = s.Size() // 2
_ = s.Values() // [1 3]
s.Clear() // []
}Contains some helper functions.
Comparator provides the following built-in type of comparator.
func IntComparator(a, b interface{}) int
func Int8Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func Int16Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func Int32Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func Int64Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func UIntComparator(a, b interface{}) int
func UInt8Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func UInt16Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func UInt32Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func UInt64Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func Float32Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func Float64Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func ByteComparator(a, b interface{}) int
func RuneComparator(a, b interface{}) int
func StringComparator(a, b interface{}) intThe meaning of the return value is as follows.
-1 => a < b
0 => a == b
1 => a > b
For custom types, you can also create a corresponding comparator.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/set/skipset"
)
type People struct {
name string
age int
}
func AgeComparator(a, b interface{}) int {
c1 := a.(People)
c2 := b.(People)
switch {
case c1.age < c2.age:
return -1
case c1.age > c2.age:
return 1
default:
return 0
}
}
func main() {
s := skipset.New(AgeComparator)
s.Add(People{"Wade", 35})
s.Add(People{"Simon", 32})
s.Add(People{"yiyi", 22})
fmt.Println(s.Values()) // [{"yiyi", 22}, {"Simon", 32}, {"Wade", 35}]
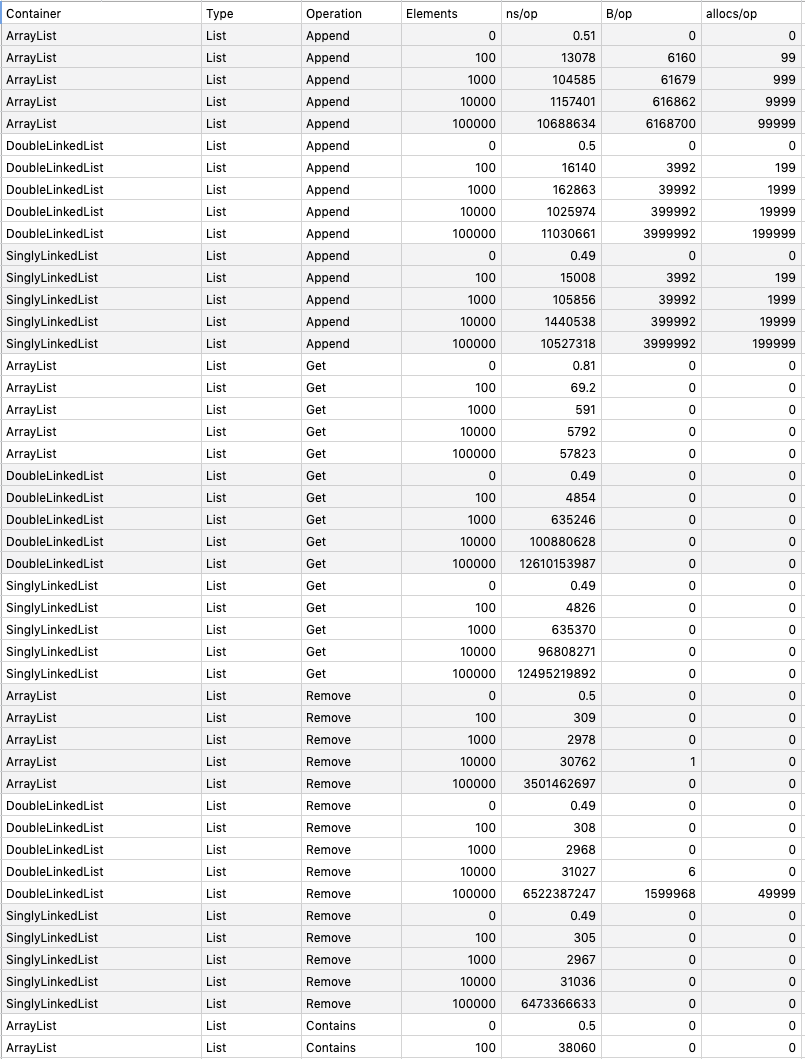
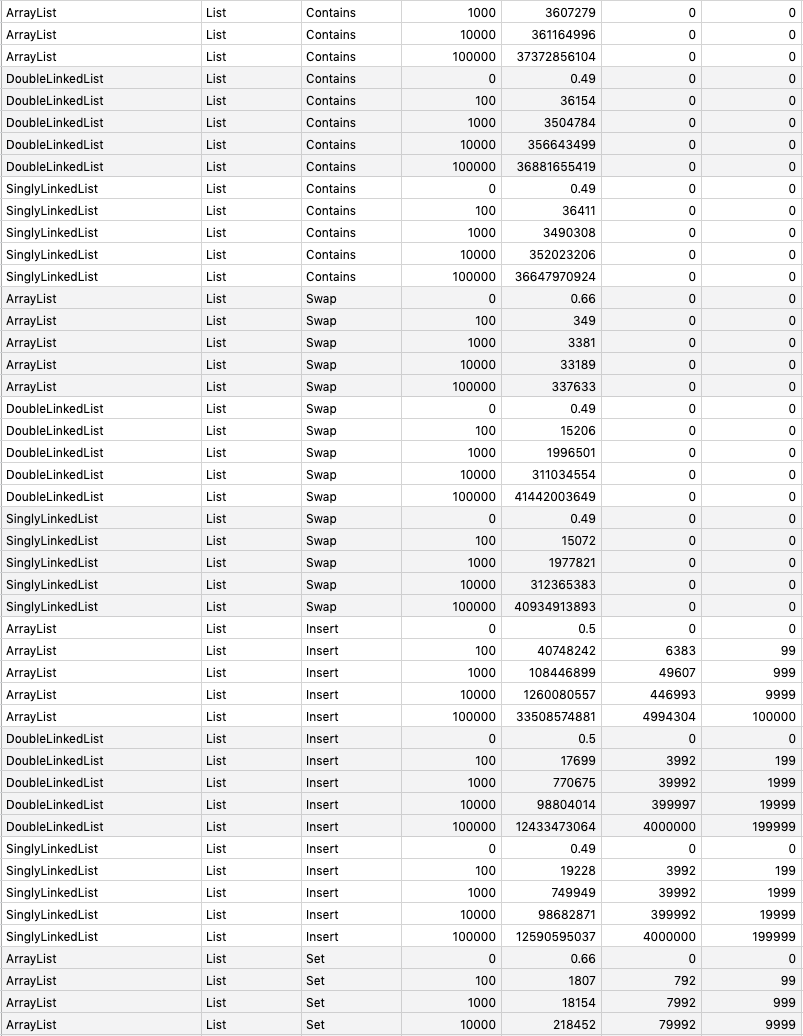
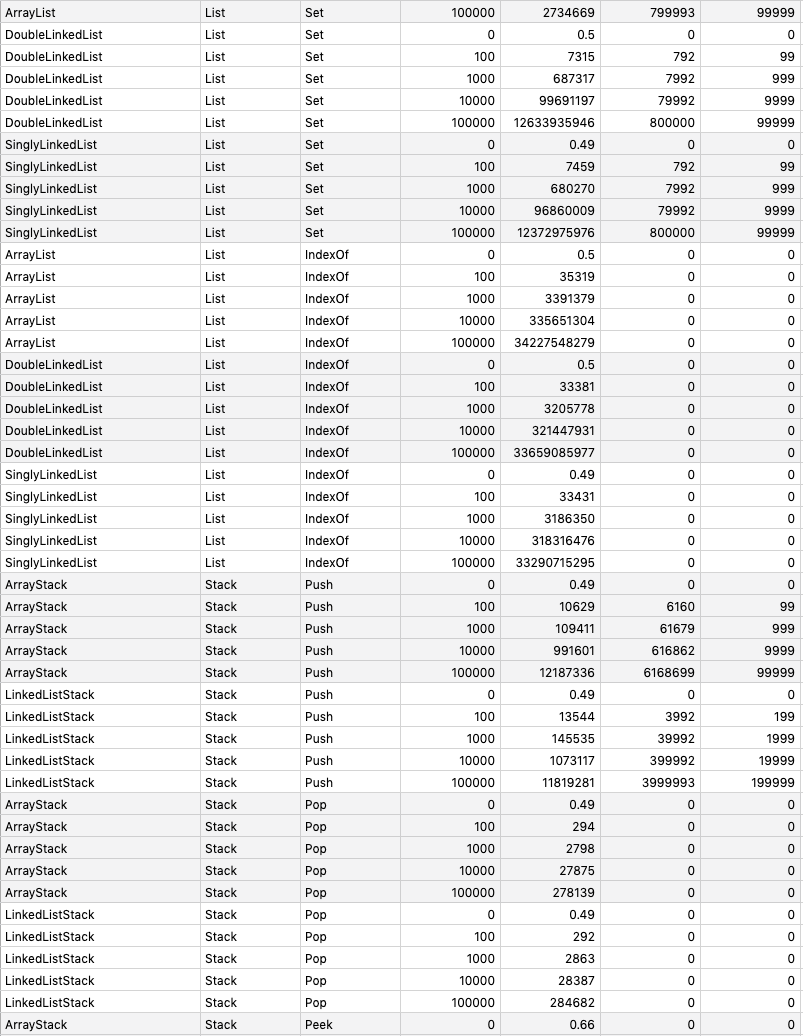
}go test -run=NO_TEST -bench=. -benchmem -benchtime 1s github.com/prprprus/ds/...