Inspire and combine from dockprom + EFK stack
Prerequisites:
- Docker Engine >= 1.13
- Docker Compose >= 1.11
docker-compose up -dContainers:
- Prometheus (metrics database)
http://<host-ip>:9090 - Prometheus-Pushgateway (push acceptor for ephemeral and batch jobs)
http://<host-ip>:9091 - AlertManager (alerts management)
http://<host-ip>:9093 - Grafana (visualize metrics)
http://<host-ip>:3000 - NodeExporter (host metrics collector)
- cAdvisor (containers metrics collector)
- Caddy (reverse proxy and basic auth provider for prometheus and alertmanager)
- Kibana is exposed on port
http://<host-ip>:5601
Please note: in this example Fluentd will run on port 8080 instead of the default 24224.
This settings has been changed to show how to configure Fluentd to listen on a different port.
Navigate to http://<host-ip>:3000 and login with user admin password admin. You can change the credentials in the compose file or by supplying the ADMIN_USER and ADMIN_PASSWORD environment variables on compose up. The config file can be added directly in grafana part like this
grafana:
image: grafana/grafana:5.2.4
env_file:
- config
and the config file format should have this content
GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_USER=admin
GF_SECURITY_ADMIN_PASSWORD=changeme
GF_USERS_ALLOW_SIGN_UP=false
If you want to change the password, you have to remove this entry, otherwise the change will not take effect
- grafana_data:/var/lib/grafana
Grafana is preconfigured with dashboards and Prometheus as the default data source:
- Name: Prometheus
- Type: Prometheus
- Url: http://prometheus:9090
- Access: proxy
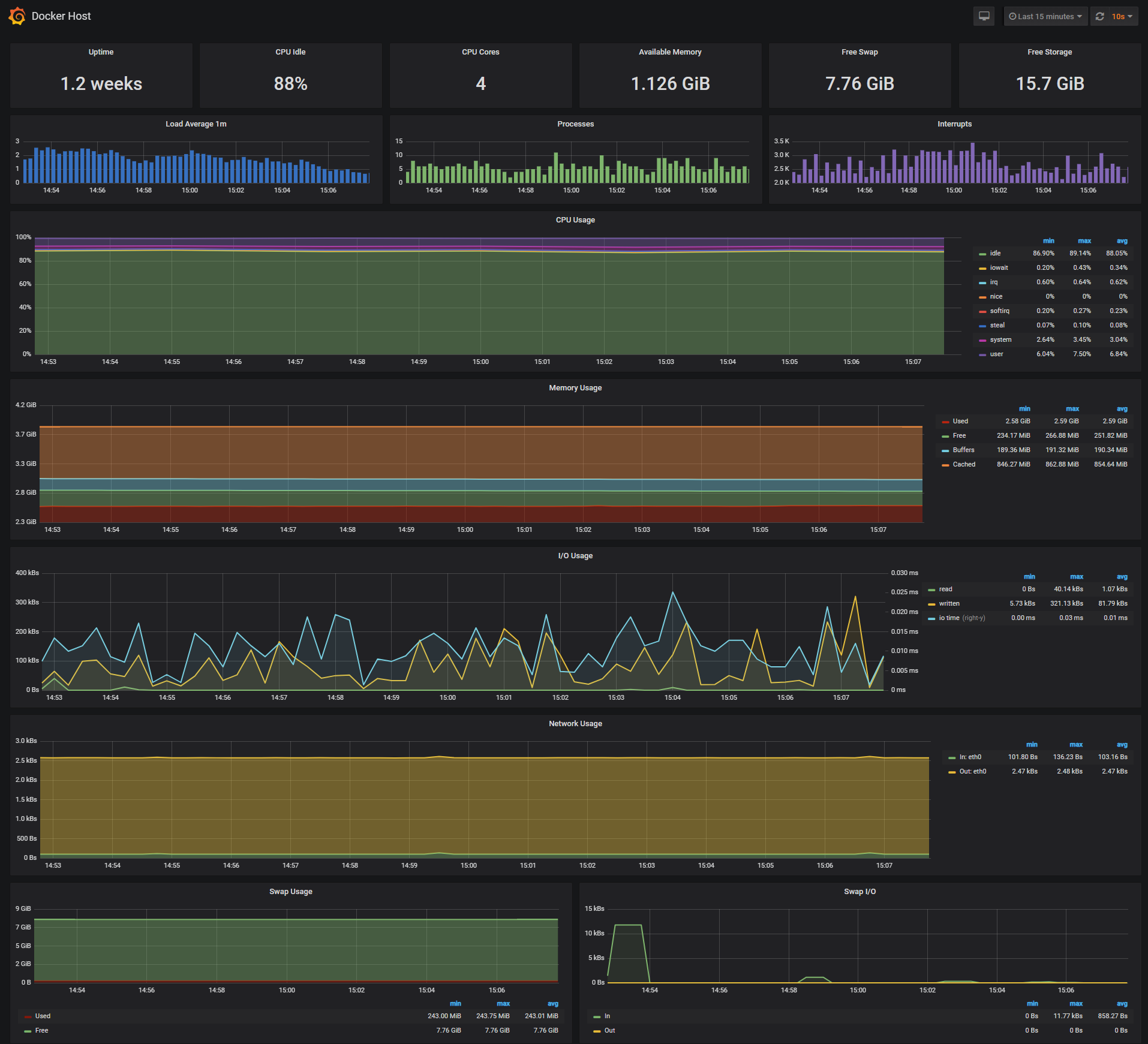
Docker Host Dashboard
The Docker Host Dashboard shows key metrics for monitoring the resource usage of your server:
- Server uptime, CPU idle percent, number of CPU cores, available memory, swap and storage
- System load average graph, running and blocked by IO processes graph, interrupts graph
- CPU usage graph by mode (guest, idle, iowait, irq, nice, softirq, steal, system, user)
- Memory usage graph by distribution (used, free, buffers, cached)
- IO usage graph (read Bps, read Bps and IO time)
- Network usage graph by device (inbound Bps, Outbound Bps)
- Swap usage and activity graphs
For storage and particularly Free Storage graph, you have to specify the fstype in grafana graph request.
You can find it in grafana/dashboards/docker_host.json, at line 480 :
"expr": "sum(node_filesystem_free_bytes{fstype=\"btrfs\"})",
I work on BTRFS, so i need to change aufs to btrfs.
You can find right value for your system in Prometheus http://<host-ip>:9090 launching this request :
node_filesystem_free_bytes
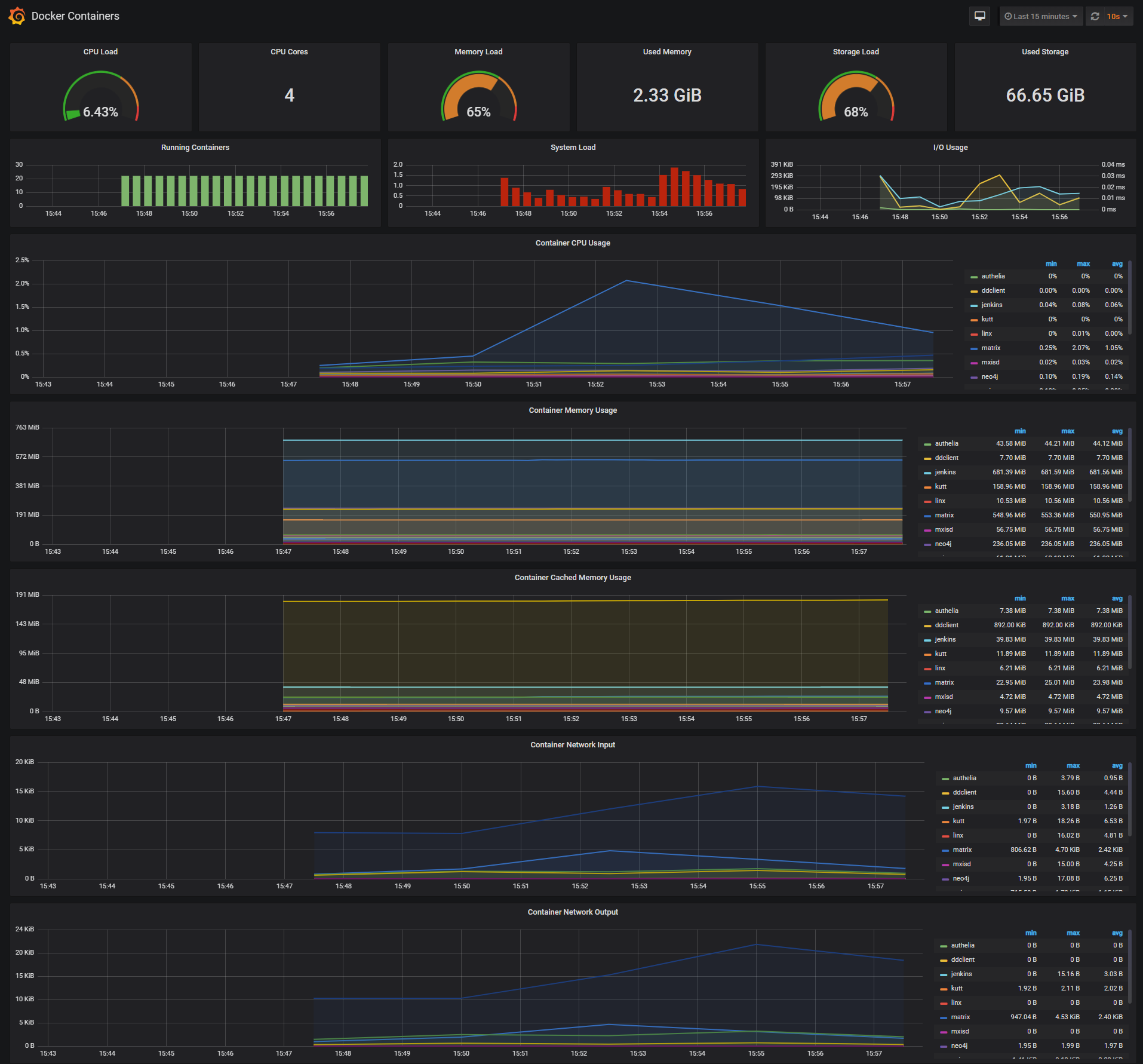
Docker Containers Dashboard
The Docker Containers Dashboard shows key metrics for monitoring running containers:
- Total containers CPU load, memory and storage usage
- Running containers graph, system load graph, IO usage graph
- Container CPU usage graph
- Container memory usage graph
- Container cached memory usage graph
- Container network inbound usage graph
- Container network outbound usage graph
Note that this dashboard doesn't show the containers that are part of the monitoring stack.
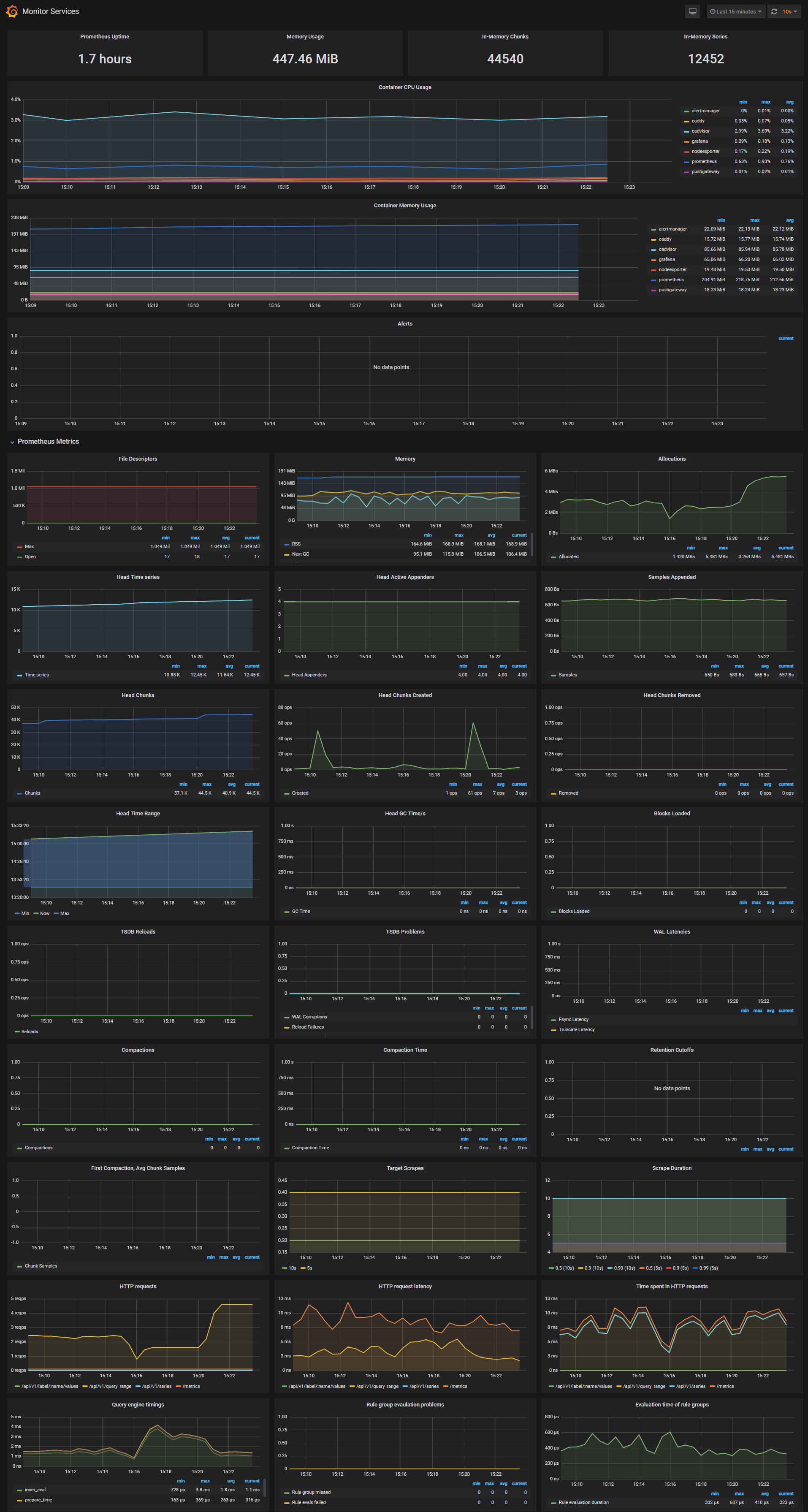
Monitor Services Dashboard
The Monitor Services Dashboard shows key metrics for monitoring the containers that make up the monitoring stack:
- Prometheus container uptime, monitoring stack total memory usage, Prometheus local storage memory chunks and series
- Container CPU usage graph
- Container memory usage graph
- Prometheus chunks to persist and persistence urgency graphs
- Prometheus chunks ops and checkpoint duration graphs
- Prometheus samples ingested rate, target scrapes and scrape duration graphs
- Prometheus HTTP requests graph
- Prometheus alerts graph
Three alert groups have been setup within the alert.rules configuration file:
- Monitoring services alerts targets
- Docker Host alerts host
- Docker Containers alerts containers
You can modify the alert rules and reload them by making a HTTP POST call to Prometheus:
curl -X POST http://admin:admin@<host-ip>:9090/-/reload
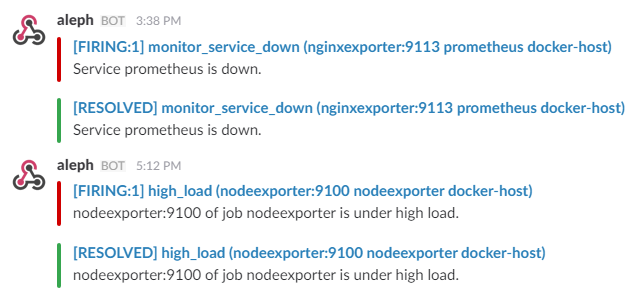
Monitoring services alerts
Trigger an alert if any of the monitoring targets (node-exporter and cAdvisor) are down for more than 30 seconds:
- alert: monitor_service_down
expr: up == 0
for: 30s
labels:
severity: critical
annotations:
summary: "Monitor service non-operational"
description: "Service {{ $labels.instance }} is down."Docker Host alerts
Trigger an alert if the Docker host CPU is under high load for more than 30 seconds:
- alert: high_cpu_load
expr: node_load1 > 1.5
for: 30s
labels:
severity: warning
annotations:
summary: "Server under high load"
description: "Docker host is under high load, the avg load 1m is at {{ $value}}. Reported by instance {{ $labels.instance }} of job {{ $labels.job }}."Modify the load threshold based on your CPU cores.
Trigger an alert if the Docker host memory is almost full:
- alert: high_memory_load
expr: (sum(node_memory_MemTotal_bytes) - sum(node_memory_MemFree_bytes + node_memory_Buffers_bytes + node_memory_Cached_bytes) ) / sum(node_memory_MemTotal_bytes) * 100 > 85
for: 30s
labels:
severity: warning
annotations:
summary: "Server memory is almost full"
description: "Docker host memory usage is {{ humanize $value}}%. Reported by instance {{ $labels.instance }} of job {{ $labels.job }}."Trigger an alert if the Docker host storage is almost full:
- alert: high_storage_load
expr: (node_filesystem_size_bytes{fstype="aufs"} - node_filesystem_free_bytes{fstype="aufs"}) / node_filesystem_size_bytes{fstype="aufs"} * 100 > 85
for: 30s
labels:
severity: warning
annotations:
summary: "Server storage is almost full"
description: "Docker host storage usage is {{ humanize $value}}%. Reported by instance {{ $labels.instance }} of job {{ $labels.job }}."Docker Containers alerts
Trigger an alert if a container is down for more than 30 seconds:
- alert: jenkins_down
expr: absent(container_memory_usage_bytes{name="jenkins"})
for: 30s
labels:
severity: critical
annotations:
summary: "Jenkins down"
description: "Jenkins container is down for more than 30 seconds."Trigger an alert if a container is using more than 10% of total CPU cores for more than 30 seconds:
- alert: jenkins_high_cpu
expr: sum(rate(container_cpu_usage_seconds_total{name="jenkins"}[1m])) / count(node_cpu_seconds_total{mode="system"}) * 100 > 10
for: 30s
labels:
severity: warning
annotations:
summary: "Jenkins high CPU usage"
description: "Jenkins CPU usage is {{ humanize $value}}%."Trigger an alert if a container is using more than 1.2GB of RAM for more than 30 seconds:
- alert: jenkins_high_memory
expr: sum(container_memory_usage_bytes{name="jenkins"}) > 1200000000
for: 30s
labels:
severity: warning
annotations:
summary: "Jenkins high memory usage"
description: "Jenkins memory consumption is at {{ humanize $value}}."The AlertManager service is responsible for handling alerts sent by Prometheus server. AlertManager can send notifications via email, Pushover, Slack, HipChat or any other system that exposes a webhook interface. A complete list of integrations can be found here.
You can view and silence notifications by accessing http://<host-ip>:9093.
The notification receivers can be configured in alertmanager/config.yml file.
To receive alerts via Slack you need to make a custom integration by choose incoming web hooks in your Slack team app page. You can find more details on setting up Slack integration here.
Copy the Slack Webhook URL into the api_url field and specify a Slack channel.
route:
receiver: 'slack'
receivers:
- name: 'slack'
slack_configs:
- send_resolved: true
text: "{{ .CommonAnnotations.description }}"
username: 'Prometheus'
channel: '#<channel>'
api_url: 'https://hooks.slack.com/services/<webhook-id>'The pushgateway is used to collect data from batch jobs or from services.
To push data, simply execute:
echo "some_metric 3.14" | curl --data-binary @- http://user:password@localhost:9091/metrics/job/some_job
Please replace the user:password part with your user and password set in the initial configuration (default: admin:admin).
If you are running macOS and you want to send sample data to test the EFK stack, you'll need [RESTed][rested].
Files are available in the examples folder.
Please note that RESTed is not strictly necessary as any other REST client application will work fine.
If you have curl client installed on your system, you can generate sample data by running:
curl -X POST -d 'json={"action":"login","userId":"5b07fbbb4e6b8"}' http://localhost:8090/myapp.log