-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 72
Ocean Current
This document describes the capabilities of the ocean current plugin and provides tutorials showing how to modify its behavior.
- The ocean current plugin is inherited from the UUV simulator. link
- The user must specify mean velocity and direction in the world SDF file.
- The plugin is integrated with the current velocity update function of vehicles at each frame.
- The current velocity updates incorporate a Gauss-Markov model to simulate noise disturbances, which is typical for ocean current representations.
Constant ocean current
- Definable with magnitude, horizontal angle, vertical angle, time period.
- "Constant" indicates that magnitude and angles remain fixed.
It is important to note that the current velocity is calculated in Gazebo's ENU reference frame since it does not recognize the SNAME convention. If you visualize the simulation output in RViz, you can subscribe to the topic /<model_name>/current_velocity_marker to see an arrow indicating the direction of the current velocity. The marker disappears if the current velocity is set to zero.
The ocean current velocity is expressed as a function of magnitude, horizontal angle and vertical angle. It can be modelled using a first-order Gauss-Markov process:
where is random noise and
(typically zero) is constant.
The world SDF consists of the following section to define ocean currents and statistics and it is self-explanatory.
<plugin name="underwater_current_plugin" filename="libuuv_underwater_current_ros_plugin.so">
<namespace>hydrodynamics</namespace>
<constant_current>
<topic>current_velocity</topic>
<velocity>
<mean>0</mean>
<min>0</min>
<max>5</max>
<mu>0.0</mu>
<noiseAmp>0.0</noiseAmp>
</velocity>
<horizontal_angle>
<mean>0</mean>
<min>-3.141592653589793238</min>
<max>3.141592653589793238</max>
<mu>0.0</mu>
<noiseAmp>0.0</noiseAmp>
</horizontal_angle>
<vertical_angle>
<mean>0</mean>
<min>-3.141592653589793238</min>
<max>3.141592653589793238</max>
<mu>0.0</mu>
<noiseAmp>0.0</noiseAmp>
</vertical_angle>
</constant_current>
</plugin>here, library file libuuv_underwater_current_ros_plugin.so is loaded with namespace 'hydrodynamic' to apply to every model included in the world with constant_current topic. (It is also possible to specify separate namespaces for each 'model'. This might be useful if each model requires different noise.) All models that are to be affected by the current must incorporate the libuuv_underwater_object_ros_plugin.so model plugin.
The Load function of UnderwaterCurrentROSPlugin.cc tries to load the UnderwaterCurrentPlugin when it starts (UnderwaterCurrentPlugin.cc).
The Load function of the UnderwaterCurrentPlugin.cc then invokes current velocity model variables(currentVelModel, currentHorzAngleModel and currentVertAngleModel which are defined as GaussmarkovProcess type in UnderwaterCurrentPlugin.hh). Also, it reads the "mean" values from the world SDF and assigns them to the var attribute of the corresponding model variables(#118). Finally, it connect its update function to the world update event and runs the following:
void UnderwaterCurrentPlugin::Update(const common::UpdateInfo & /** _info */)
{
#if GAZEBO_MAJOR_VERSION >= 8
common::Time time = this->world->SimTime();
#else
common::Time time = this->world->GetSimTime();
#endif
// Calculate the flow velocity and the direction using the Gauss-Markov
// model
// Update current velocity and angles
double currentVelMag = this->currentVelModel.Update(time.Double());
double horzAngle = this->currentHorzAngleModel.Update(time.Double());
double vertAngle = this->currentVertAngleModel.Update(time.Double());
// Generating the current velocity vector as in the NED frame
this->currentVelocity = ignition::math::Vector3d(
currentVelMag * cos(horzAngle) * cos(vertAngle),
currentVelMag * sin(horzAngle) * cos(vertAngle),
currentVelMag * sin(vertAngle));
// Update time stamp
this->lastUpdate = time;
this->PublishCurrentVelocity();
}here, at each simulation time, the current velocity model variables(currentVelModel, currentHorzAngleModel and currentVertAngleModel) are updated and currentVelocity is calculated in the NED frame to be published.
Lastly, the GaussmarkovProcess type variable is updated in the following lines which implement a straightforward interpretation of the model. The max/min bounds and noise are defined in the world SDF.
double GaussMarkovProcess::Update(double _time)
{
double step = _time - this->lastUpdate;
double random = static_cast<double>(static_cast<double>(rand()) / RAND_MAX)
- 0.5;
this->var = (1 - step * this->mu) * this->var + this->noiseAmp * random;
if (this->var >= this->max)
this->var = this->max;
if (this->var <= this->min)
this->var = this->min;
this->lastUpdate = _time;
return this->var;
}- Start standard ocean_world world without ocean current
roslaunch uuv_dave uuv_dave.launch - To set the ocean current using the
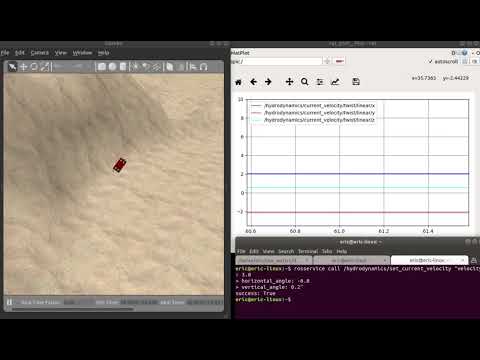
/hydrodynamic/current_velocitytopic, type following commands in another terminal.orrosservice call /hydrodynamics/set_current_velocity "velocity: 1.0 horizontal_angle: -0.8 vertical_angle: 0.2"After entering these commands, the REXROV vehicle will start to drift.rosservice call /hydrodynamics/set_current_velocity "velocity: 1.0" rosservice call /hydrodynamics/set_current_horz_angle "angle: -0.8" rosservice call /hydrodynamics/set_current_vert_angle "angle: 0.2"- The angles are defined in Gazebo's ENU reference frame, within a range from 0 to 3.14.
- You can plot the value using rqt_plot.
rqt_plot /hydrodynamics/current_velocity/twist/linear - The same method can be used to add noise generated by the Gauss-Markov model:
rosservice call /hydrodynamics/set_current_velocity_model "{mean: 1.0, min: 0.0, max: 2.0, noise: 0.0, mu: 0.0}" rosservice call /hydrodynamics/set_current_horz_angle_model "{mean: -0.8, min: -1.0, max: 0.0, noise: 0.0, mu: 0.0}" rosservice call /hydrodynamics/set_current_vert_angle_model "{mean: 0.2, min: 0.0, max: 0.3, noise: 0.0, mu: 0.0}" - Alternatively, the following commands can be used to set the current during a fix period of time:
roslaunch uuv_control_utils set_timed_current_perturbation.launch starting_time:=0.0 end_time:=10.0 current_vel:=1.0 horizontal_angle:=10.0 vertical_angle:=30
(Note in this case the units of angles are in degrees.)
Following the tutorial above:
- set velocity, horizontal and vertical angles to 1.0, -0.8 and 0.2.
- visualize the current velocity values using rqt_plot Now run the command below to alter the mean velocity:
rosservice call /hydrodynamics/set_current_velocity "velocity: 2.0"
You should see the change reflected in your rqt_plot display:

Similarly, you can dynamically alter the parameters used for generating noise. First run
rosservice call /hydrodynamics/set_current_velocity_model "{mean: 1.0, min: 0.0, max: 2.0, noise: 0.0, mu: 0.0}"
to set initial noise parameters. Next, alter these by running:
rosservice call /hydrodynamics/set_current_velocity_model "{mean: 1.0, min: 0.0, max: 2.0, noise: 10.0, mu: 0.0}"
The change will register on your rqt_plot display. It should looks something like this:

- In order for a model to be affected by current, its SDF description must include the Underwater Object plugin (
libuuv_underwater_object_ros_plugin.so). - The following SDF snippet corresponds to the Rexrov UUV provided with the UUV Simulator.
- The
flow_velocity_topicelement specifies the ROS topic (including namespace) to which the plugin will subscribe for current information. - Other elements describe the model's hydrodynamic characteristics and are documented elsewhere.
<plugin name='uuv_plugin' filename='libuuv_underwater_object_ros_plugin.so'>
<fluid_density>1028.0</fluid_density>
<flow_velocity_topic>hydrodynamics/current_velocity</flow_velocity_topic>
<debug>0</debug>
<link name='rexrov/base_link'>
<neutrally_buoyant>0</neutrally_buoyant>
<volume>1.83826</volume>
<box>
<width>1.5</width>
<length>2.6</length>
<height>1.6</height>
</box>
<center_of_buoyancy>0.0 0.0 0.3</center_of_buoyancy>
<hydrodynamic_model>
<type>fossen</type>
<added_mass>779.79 -6.8773 -103.32 8.5426 -165.54 -7.8033 -6.8773 1222 51.29 409.44 -5.8488 62.726 -103.32 51.29 3659.9 6.1112 -386.42 10.774 8.5426 409.44 6.1112 534.9 -10.027 21.019 -165.54 -5.8488 -386.42 -10.027 842.69 -1.1162 -7.8033 62.726 10.775 21.019 -1.1162 224.32</added_mass>
<linear_damping>-74.82 -69.48 -728.4 -268.8 -309.77 -105</linear_damping>
<quadratic_damping>-748.22 -992.53 -1821.01 -672 -774.44 -523.27</quadratic_damping>
</hydrodynamic_model>
</link>
<robotNamespace>/rexrov/</robotNamespace>
</plugin>[1] T. I. Fossen, “Handbook of Marine Craft Hydrodynamics and Motion Control,” Apr. 2011.. (pp. 223-4)