Releases: fmtlib/fmt
8.1.1
-
Restored ABI compatibility with version 8.0.x (#2695, #2696). Thanks @saraedum (Julian Rüth).
-
Fixed chrono formatting on big endian systems (#2698, #2699). Thanks @phprus (Vladislav Shchapov) and @xvitaly (Vitaly Zaitsev).
-
Fixed a linkage error with mingw (#2691, #2692). Thanks @rbberger (Richard Berger).
8.1.0
-
Optimized chrono formatting (#2500, #2537, #2541, #2544, #2550, #2551, #2576, #2577, #2586, #2591, #2594, #2602, #2617, #2628, #2633, #2670, #2671).
Processing of some specifiers such as
%zand%Yis now up to 10-20 times faster, for example on GCC 11 with libstdc++:---------------------------------------------------------------------------- Benchmark Before After ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- FMTFormatter_z 261 ns 26.3 ns FMTFormatterCompile_z 246 ns 11.6 ns FMTFormatter_Y 263 ns 26.1 ns FMTFormatterCompile_Y 244 ns 10.5 ns ----------------------------------------------------------------------------Thanks @phprus (Vladislav Shchapov) and @toughengineer (Pavel Novikov).
-
Implemented subsecond formatting for chrono durations (#2623). For example (godbolt):
#include <fmt/chrono.h> int main() { fmt::print("{:%S}", std::chrono::milliseconds(1234)); }
prints "01.234".
Thanks @matrackif.
-
Fixed handling of precision 0 when formatting chrono durations (#2587, #2588). Thanks @lukester1975.
-
Fixed an overflow on invalid inputs in the
tmformatter (#2564). Thanks @phprus (Vladislav Shchapov). -
Added
fmt::group_digitsthat formats integers with a non-localized digit separator (comma) for groups of three digits. For example (godbolt):#include <fmt/format.h> int main() { fmt::print("{} dollars", fmt::group_digits(1000000)); }
prints "1,000,000 dollars".
-
Added support for faint, conceal, reverse and blink text styles (#2394):
blink.mp4
Thanks @benit8 (Benoît Lormeau) and @data-man (Dmitry Atamanov).
-
Added experimental support for compile-time floating point formatting (#2426, #2470). It is currently limited to the header-only mode. Thanks @alexezeder (Alexey Ochapov).
-
Added UDL-based named argument support to compile-time format string checks (#2640, #2649). For example (godbolt):
#include <fmt/format.h> int main() { using namespace fmt::literals; fmt::print("{answer:s}", "answer"_a=42); }
gives a compile-time error on compilers with C++20
constevaland non-type template parameter support (gcc 10+) becausesis not a valid format specifier for an integer.Thanks @alexezeder (Alexey Ochapov).
-
Implemented escaping of string range elements. For example (godbolt):
#include <fmt/ranges.h> #include <vector> int main() { fmt::print("{}", std::vector<std::string>{"\naan"}); }
is now printed as:
["\naan"]instead of:
[" aan"] -
Switched to JSON-like representation of maps and sets for consistency with Python's
str.format. For example (godbolt):#include <fmt/ranges.h> #include <map> int main() { fmt::print("{}", std::map<std::string, int>{{"answer", 42}}); }
is now printed as:
{"answer": 42} -
Extended
fmt::jointo support C++20-only ranges (#2549). Thanks @BRevzin (Barry Revzin). -
Optimized handling of non-const-iterable ranges and implemented initial support for non-const-formattable types.
-
Disabled implicit conversions of scoped enums to integers that was accidentally introduced in earlier versions (#1841).
-
Deprecated implicit conversion of
[const] signed char*and[const] unsigned char*to C strings. -
Deprecated
_format, a legacy UDL-based format API (#2646). Thanks @alexezeder (Alexey Ochapov). -
Marked
format,formatted_sizeandto_stringas[[nodiscard]](#2612). @0x8000-0000 (Florin Iucha). -
Added missing diagnostic when trying to format function and member pointers as well as objects convertible to pointers which is explicitly disallowed (#2598, #2609, #2610). Thanks @AlexGuteniev (Alex Guteniev).
-
Optimized writing to a contiguous buffer with
format_to_n(#2489). Thanks @Roman-Koshelev. -
Optimized writing to non-
charbuffers (#2477). Thanks @Roman-Koshelev. -
Decimal point is now localized when using the
Lspecifier. -
Improved floating point formatter implementation (#2498, #2499). Thanks @Roman-Koshelev.
-
Fixed handling of very large precision in fixed format (#2616).
-
Made a table of cached powers used in FP formatting static (#2509). Thanks @jk-jeon (Junekey Jeon).
-
Resolved a lookup ambiguity with C++20 format-related functions due to ADL (#2639, #2641). Thanks @mkurdej (Marek Kurdej).
-
Removed unnecessary inline namespace qualification (#2642, #2643). Thanks @mkurdej (Marek Kurdej).
-
Implemented argument forwarding in
format_to_n(#2462, #2463). Thanks @owent (WenTao Ou). -
Fixed handling of implicit conversions in
fmt::to_stringand format string compilation (#2565). -
Changed the default access mode of files created by
fmt::output_fileto-rw-r--r--for consistency withfopen(#2530). -
Make
fmt::ostream::flushpublic (#2435). -
Improved C++14/17 attribute detection (#2615). Thanks @AlexGuteniev (Alex Guteniev).
-
Improved
constevaldetection for MSVC (#2559). Thanks @DanielaE (Daniela Engert). -
Improved documentation (#2406, #2446, #2493, #2513, #2515, #2522, #2562, #2575, #2606, #2620, #2676). Thanks @sobolevn (Nikita Sobolev), @UnePierre (Max FERGER), @zhsj, @phprus (Vladislav Shchapov), @ericcurtin (Eric Curtin), @Lounarok.
-
Improved fuzzers and added a fuzzer for chrono timepoint formatting (#2461, #2469). @pauldreik (Paul Dreik),
-
Added the
FMT_SYSTEM_HEADERSCMake option setting which marks {fmt}'s headers as system. It can be used to suppress warnings (#2644, #2651). Thanks @alexezeder (Alexey Ochapov). -
Added the Bazel build system support (#2505, #2516). Thanks @Vertexwahn.
-
Improved build configuration and tests (#2437, #2558, #2648, #2650, #2663, #2677). Thanks @DanielaE (Daniela Engert), @alexezeder (Alexey Ochapov), @phprus (Vladislav Shchapov).
-
Fixed various warnings and compilation issues (#2353, #2356, #2399, #2408, #2414, #2427, #2432, #2442, #2434, #2439, #2447, #2450, #2455, #2465, #2472, #2474, #2476, #2478, #2479, #2481, #2482, #2483, #2490, #2491, #2510, #2518, #2528, #2529, #2539, #2540, #2545, #2555, #2557, #2570, #2573, #2582, #2605, #2611, #2647, #2627, #2630, #2635, #2638, #2653, #2654, #2661, #2664, #2684). Thanks @DanielaE (Daniela Engert), @mwinterb, @cdacamar (Cameron DaCamara), @TrebledJ (Johnathan), @bodomartin (brm), @cquammen (Cory Quammen), @white238 (Chris White), @mmarkeloff (Max), @palacaze (Pierre-Antoine Lacaze), @jcelerier (Jean-Michaël Celerier), @mborn-adi (Mathias Born), @BrukerJWD (Jonathan W), @spyridon97 (Spiros Tsalikis), @phprus (Vladislav Shchapov), @oliverlee (Oliver Lee), @joshessman-llnl (Josh Essman), @akohlmey (Axel Kohlmeyer), @timkalu, @olupton (Olli Lupton), @Acretock, @alexezeder (Alexey Ochapov), @andrewcorrigan (Andrew Corrigan), @lucpelletier, @HazardyKnusperkeks (Björn Schäpers).
8.0.1
-
Fixed the version number in the inline namespace (#2374).
-
Added a missing presentation type check for
std::string(#2402). -
Fixed a linkage error when mixing code built with clang and gcc (#2377).
-
Fixed documentation issues (#2396, #2403, #2406). Thanks @mkurdej (Marek Kurdej).
-
Removed dead code in FP formatter ( #2398). Thanks @javierhonduco (Javier Honduvilla Coto).
-
Fixed various warnings and compilation issues (#2351, #2359, #2365, #2368, #2370, #2376, #2381, #2382, #2386, #2389, #2395, #2397, #2400 #2401, #2407). Thanks @zx2c4 (Jason A. Donenfeld), @AidanSun05 (Aidan Sun), @mattiasljungstrom (Mattias Ljungström), @joemmett (Jonathan Emmett), @erengy (Eren Okka), @patlkli (Patrick Geltinger), @gsjaardema (Greg Sjaardema), @phprus (Vladislav Shchapov).
8.0.0
-
Enabled compile-time format string check by default. For example (godbolt):
#include <fmt/core.h> int main() { fmt::print("{:d}", "I am not a number"); }
gives a compile-time error on compilers with C++20
constevalsupport (gcc 10+, clang 11+) becausedis not a valid format specifier for a string.To pass a runtime string wrap it in
fmt::runtime:fmt::print(fmt::runtime("{:d}"), "I am not a number");
-
Added compile-time formatting (#2019, #2044, #2056, #2072, #2075, #2078, #2129, #2326). For example (godbolt):
#include <fmt/compile.h> consteval auto compile_time_itoa(int value) -> std::array<char, 10> { auto result = std::array<char, 10>(); fmt::format_to(result.data(), FMT_COMPILE("{}"), value); return result; } constexpr auto answer = compile_time_itoa(42);
Most of the formatting functionality is available at compile time with a notable exception of floating-point numbers and pointers. Thanks @alexezeder (Alexey Ochapov).
-
Optimized handling of format specifiers during format string compilation. For example, hexadecimal formatting (
"{:x}") is now 3-7x faster than before when usingformat_towith format string compilation and a stack-allocated buffer (#1944).Before (7.1.3):
---------------------------------------------------------------------------- Benchmark Time CPU Iterations ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- FMTCompileOld/0 15.5 ns 15.5 ns 43302898 FMTCompileOld/42 16.6 ns 16.6 ns 43278267 FMTCompileOld/273123 18.7 ns 18.6 ns 37035861 FMTCompileOld/9223372036854775807 19.4 ns 19.4 ns 35243000 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------After (8.x):
---------------------------------------------------------------------------- Benchmark Time CPU Iterations ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- FMTCompileNew/0 1.99 ns 1.99 ns 360523686 FMTCompileNew/42 2.33 ns 2.33 ns 279865664 FMTCompileNew/273123 3.72 ns 3.71 ns 190230315 FMTCompileNew/9223372036854775807 5.28 ns 5.26 ns 130711631 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------It is even faster than
std::to_charsfrom libc++ compiled with clang on macOS:---------------------------------------------------------------------------- Benchmark Time CPU Iterations ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- ToChars/0 4.42 ns 4.41 ns 160196630 ToChars/42 5.00 ns 4.98 ns 140735201 ToChars/273123 7.26 ns 7.24 ns 95784130 ToChars/9223372036854775807 8.77 ns 8.75 ns 75872534 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------In other cases, especially involving
std::stringconstruction, the speed up is usually lower because handling format specifiers takes a smaller fraction of the total time. -
Added the
_cfuser-defined literal to represent a compiled format string. It can be used instead of theFMT_COMPILEmacro (#2043, #2242):#include <fmt/compile.h> using namespace fmt::literals; auto s = fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{}"), 42); // 🙁 not modern auto s = fmt::format("{}"_cf, 42); // 🙂 modern as hell
It requires compiler support for class types in non-type template parameters (a C++20 feature) which is available in GCC 9.3+. Thanks @alexezeder (Alexey Ochapov).
-
Format string compilation now requires
formatfunctions offormatterspecializations for user-defined types to beconst:template <> struct fmt::formatter<my_type>: formatter<string_view> { template <typename FormatContext> auto format(my_type obj, FormatContext& ctx) const { // Note const here. // ... } };
-
Added UDL-based named argument support to format string compilation (#2243, #2281). For example:
#include <fmt/compile.h> using namespace fmt::literals; auto s = fmt::format(FMT_COMPILE("{answer}"), "answer"_a = 42);
Here the argument named "answer" is resolved at compile time with no runtime overhead. Thanks @alexezeder (Alexey Ochapov).
-
Added format string compilation support to
fmt::print(#2280, #2304). Thanks @alexezeder (Alexey Ochapov). -
Added initial support for compiling {fmt} as a C++20 module (#2235, #2240, #2260, #2282, #2283, #2288, #2298, #2306, #2307, #2309, #2318, #2324, #2332, #2340). Thanks @DanielaE (Daniela Engert).
-
Made symbols private by default reducing shared library size (#2301). For example there was a ~15% reported reduction on one platform. Thanks @sergiud (Sergiu Deitsch).
-
Optimized includes making the result of preprocessing
fmt/format.h~20% smaller with libstdc++/C++20 and slightly improving build times (#1998). -
Added support of ranges with non-const
begin/end(#1953). Thanks @kitegi (sarah). -
Added support of
std::byteand other formattable types tofmt::join(#1981, #2040, #2050, #2262). For example:#include <fmt/format.h> #include <cstddef> #include <vector> int main() { auto bytes = std::vector{std::byte(4), std::byte(2)}; fmt::print("{}", fmt::join(bytes, "")); }
prints "42".
Thanks @kamibo (Camille Bordignon).
-
Implemented the default format for
std::chrono::system_clock(#2319, #2345). For example:#include <fmt/chrono.h> int main() { fmt::print("{}", std::chrono::system_clock::now()); }
prints "2021-06-18 15:22:00" (the output depends on the current date and time). Thanks @sunmy2019.
-
Made more chrono specifiers locale independent by default. Use the
'L'specifier to get localized formatting. For example:#include <fmt/chrono.h> int main() { std::locale::global(std::locale("ru_RU.UTF-8")); auto monday = std::chrono::weekday(1); fmt::print("{}\n", monday); // prints "Mon" fmt::print("{:L}\n", monday); // prints "пн" }
-
Improved locale handling in chrono formatting (#2337, #2349, #2350). Thanks @phprus (Vladislav Shchapov).
-
Deprecated
fmt/locale.hmoving the formatting functions that take a locale tofmt/format.h(char) andfmt/xchar(other overloads). This doesn't introduce a dependency on<locale>so there is virtually no compile time effect. -
Made parameter order in
vformat_toconsistent withformat_to(#2327). -
Added support for time points with arbitrary durations (#2208). For example:
#include <fmt/chrono.h> int main() { using tp = std::chrono::time_point< std::chrono::system_clock, std::chrono::seconds>; fmt::print("{:%S}", tp(std::chrono::seconds(42))); }
prints "42".
-
Formatting floating-point numbers no longer produces trailing zeros by default for consistency with
std::format. For example:#include <fmt/core.h> int main() { fmt::print("{0:.3}", 1.1); }
prints "1.1". Use the
'#'specifier to keep trailing zeros. -
Dropped a limit on the number of elements in a range and replaced
{}with[]as range delimiters for consistency with Python'sstr.format. -
The
'L'specifier for locale-specific numeric formatting can now be combined with presentation specifiers as instd::format. For example:#include <fmt/core.h> #include <locale> int main() { std::locale::global(std::locale("fr_FR.UTF-8")); fmt::print("{0:.2Lf}", 0.42); }
prints "0,42". The deprecated
'n'specifier has been removed. -
Made the
0specifier ignored for infinity and NaN (#2305, #2310). Thanks @Liedtke (Matthias Liedtke). -
Made the hexfloat formatting use the right alignment by default (#2308, #2317). Thanks @Liedtke (Matthias Liedtke).
-
Removed the deprecated numeric alignment (
'='). Use the'0'specifier instead. -
Removed the deprecated
fmt/posix.hheader that has been replaced withfmt/os.h. -
Removed the deprecated
format_to_n_context,format_to_n_argsandmake_format_to_n_args. They have been replaced withformat_context,format_argsandmake_format_argsrespectively. -
Moved
wchar_t-specific functions and types tofmt/xchar.h. You can defineFMT_DEPRECATED_INCLUDE_XCHARto automatically includefmt/xchar.hfromfmt/format.hbut this will be disabled in the next major release. -
Fixed handling of the
'+'spec...
7.1.3
7.1.2
7.1.1
-
Fixed ABI compatibility with 7.0.x (#1961).
-
Added the
FMT_ARM_ABI_COMPATIBILITYmacro to work around ABI incompatibility between GCC and Clang on ARM (#1919). -
Worked around a SFINAE bug in GCC 8 (#1957).
-
Fixed linkage errors when building with GCC's LTO (#1955).
-
Fixed a compilation error when building without
__builtin_clzor equivalent (#1968). Thanks @tohammer (Tobias Hammer). -
Fixed a sign conversion warning (#1964). Thanks @OptoCloud.
7.1.0
-
Switched from Grisu3 to Dragonbox for the default floating-point formatting which gives the shortest decimal representation with round-trip guarantee and correct rounding (#1882, #1887, #1894). This makes {fmt} up to 20-30x faster than common implementations of
std::ostringstreamandsprintfon dtoa-benchmark and faster than double-conversion and Ryū: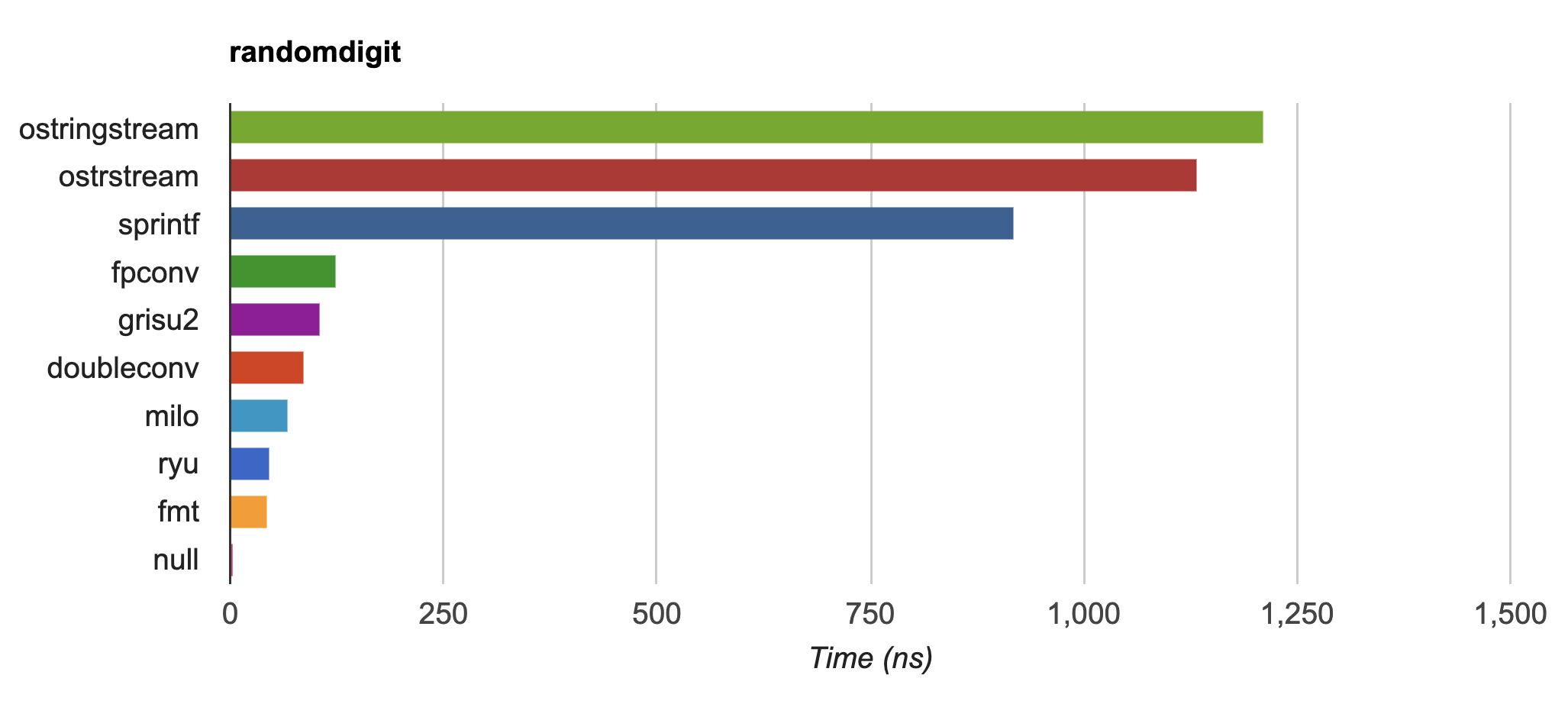 It is possible to get even better performance at the cost of larger binary size by compiling with the
It is possible to get even better performance at the cost of larger binary size by compiling with the FMT_USE_FULL_CACHE_DRAGONBOXmacro set to 1. Thanks @jk-jeon (Junekey Jeon). -
Added an experimental unsynchronized file output API which, together with format string compilation, can give 5-9 times speed up compared to fprintf on common platforms (godbolt):
#include <fmt/os.h> int main() { auto f = fmt::output_file("guide"); f.print("The answer is {}.", 42); }
-
Added a formatter for
std::chrono::time_point<system_clock>(#1819, #1837). For example (godbolt):#include <fmt/chrono.h> int main() { auto now = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); fmt::print("The time is {:%H:%M:%S}.\n", now); }
Thanks @adamburgess (Adam Burgess).
-
Added support for ranges with non-const
begin/endtofmt::join(#1784, #1786). For example (godbolt):#include <fmt/ranges.h> #include <range/v3/view/filter.hpp> int main() { using std::literals::string_literals::operator""s; auto strs = std::array{"a"s, "bb"s, "ccc"s}; auto range = strs | ranges::views::filter( [] (const std::string &x) { return x.size() != 2; } ); fmt::print("{}\n", fmt::join(range, "")); }
prints "accc". Thanks @tonyelewis (Tony E Lewis).
-
Added a
memory_buffer::appendoverload that takes a range (#1806). Thanks @BRevzin (Barry Revzin). -
Improved handling of single code units in
FMT_COMPILE. For example:#include <fmt/compile.h> char* f(char* buf) { return fmt::format_to(buf, FMT_COMPILE("x{}"), 42); }
compiles to just (godbolt):
_Z1fPc: movb $120, (%rdi) xorl %edx, %edx cmpl $42, _ZN3fmt2v76detail10basic_dataIvE23zero_or_powers_of_10_32E+8(%rip) movl $3, %eax seta %dl subl %edx, %eax movzwl _ZN3fmt2v76detail10basic_dataIvE6digitsE+84(%rip), %edx cltq addq %rdi, %rax movw %dx, -2(%rax) retHere a single
movinstruction writes'x'($120) to the output buffer. -
Added dynamic width support to format string compilation (#1809).
-
Improved error reporting for unformattable types: now you'll get the type name directly in the error message instead of the note:
#include <fmt/core.h> struct how_about_no {}; int main() { fmt::print("{}", how_about_no()); }
Error (godbolt):
fmt/core.h:1438:3: error: static_assert failed due to requirement 'fmt::v7::formattable<how_about_no>()' "Cannot format an argument. To make type T formattable provide a formatter<T> specialization: https://fmt.dev/latest/api.html#udt" ... -
Added the make_args_checked function template that allows you to write formatting functions with compile-time format string checks and avoid binary code bloat (godbolt):
void vlog(const char* file, int line, fmt::string_view format, fmt::format_args args) { fmt::print("{}: {}: ", file, line); fmt::vprint(format, args); } template <typename S, typename... Args> void log(const char* file, int line, const S& format, Args&&... args) { vlog(file, line, format, fmt::make_args_checked<Args...>(format, args...)); } #define MY_LOG(format, ...) \ log(__FILE__, __LINE__, FMT_STRING(format), __VA_ARGS__) MY_LOG("invalid squishiness: {}", 42);
-
Replaced
snprintffallback with a faster internal IEEE 754floatanddoubleformatter for arbitrary precision. For example (godbolt):#include <fmt/core.h> int main() { fmt::print("{:.500}\n", 4.9406564584124654E-324); }
prints
4.9406564584124654417656879286822137236505980261432476442558568250067550727020875186529983636163599237979656469544571773092665671035593979639877479601078187812630071319031140452784581716784898210368871863605699873072305000638740915356498438731247339727316961514003171538539807412623856559117102665855668676818703956031062493194527159149245532930545654440112748012970999954193198940908041656332452475714786901472678015935523861155013480352649347201937902681071074917033322268447533357208324319360923829e-324. -
Made
format_to_nandformatted_sizepart of the core API (godbolt):#include <fmt/core.h> int main() { char buffer[10]; auto result = fmt::format_to_n(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "{}", 42); }
-
Added
fmt::format_to_noverload with format string compilation (#1764, #1767, #1869). For example (godbolt):#include <fmt/compile.h> int main() { char buffer[8]; fmt::format_to_n(buffer, sizeof(buffer), FMT_COMPILE("{}"), 42); }
Thanks @Kurkin (Dmitry Kurkin), @alexezeder (Alexey Ochapov).
-
Added
fmt::format_tooverload that taketext_style(#1593, #1842, #1843). For example (godbolt):#include <fmt/color.h> int main() { std::string out; fmt::format_to(std::back_inserter(out), fmt::emphasis::bold | fg(fmt::color::red), "The answer is {}.", 42); }
Thanks @Naios (Denis Blank).
-
Made the
#specifier emit trailing zeros in addition to the decimal point (#1797). For example (godbolt):#include <fmt/core.h> int main() { fmt::print("{:#.2g}", 0.5); }
prints
0.50. -
Changed the default floating point format to not include
.0for consistency withstd::formatandstd::to_chars(#1893, #1943). It is possible to get the decimal point and trailing zero with the#specifier. -
Fixed an issue with floating-point formatting that could result in addition of a non-significant trailing zero in rare cases e.g.
1.00e-34instead of1.0e-34(#1873, #1917). -
Made
fmt::to_stringfallback onostreaminsertion operator if theformatterspecialization is not provided (#1815, #1829). Thanks @alexezeder (Alexey Ochapov). -
Added support for the append mode to the experimental file API and improved
fcntl.hdetection. (#1847, #1848). Thanks @t-wiser. -
Fixed handling of types that have both an implicit conversion operator and an overloaded
ostreaminsertion operator (#1766). -
Fixed a slicing issue in an internal iterator type (#1822). Thanks @BRevzin (Barry Revzin).
-
Fixed an issue in locale-specific integer formatting (#1927).
-
Improved
FMT_ALWAYS_INLINE(#1878). Thanks @jk-jeon (Junekey Jeon). -
Removed dependency on
windows.h(#1900). Thanks @bernd5 (Bernd Baumanns). -
Optimized counting of decimal digits on MSVC (#1890). Thanks @mwinterb.
-
Improved documentation (#1772, #1775, #1792, #1838, #1888, #1918, #1939). Thanks @leolchat (Léonard Gérard), @pepsiman (Malcolm Parsons), @Klaim (Joël Lamotte), @ravijanjam (Ravi J), @francesco-st, @udnaan (Adnan).
-
Added the
FMT_REDUCE_INT_INSTANTIATIONSCMake option that reduces the binary code size at the cost of some integer formatting performance. This can be useful for extremely memory-constrained embedded systems (#1778, #1781). Thanks @kammce (Khalil Estell). -
Added the
FMT_USE_INLINE_NAMESPACESmacro to control usage of inline namespaces (#1945). Thanks @darklukee. -
Improved build configuration (#1760, #1770, #1779, #1783, #1823). Thanks @dvetutnev (Dmitriy Vetutnev), @xvitaly (Vitaly Zaitsev), @tambry (Raul Tambre), @medithe, @martinwuehrer (Martin Wührer).
-
Fixed various warnings and compilation issues (#1790, #1802, #1808, #1810, #1811, #1812, #1814, #1816, #1817, #1818, #1825, #1836, #1855, #1856, #1860, #1877, #1879, #1880, #1896, #1897, #1898, #1904, #1908, #1911, #1912, #1928, #1929, #1935 #1937, #1942, #1949). Thanks @TheQwertiest, @medithe, [@martinwuehrer (Martin Wührer)](h...